by Gary Mintchell | Feb 19, 2020 | Uncategorized
While at the Hannover Messe Preview last week in Germany, I talked with the representatives of a German consortium with the interesting name of “it’s OWL”. Following are some thoughts from the various organizations that compose the consortium.
Intelligent production and new business models
Artificial Intelligence is of crucial importance for the competitiveness of industry. In the Leading-Edge Cluster it’s OWL six research institutes cooperate with more than 100 companies to develop practical solutions for small and medium-sized businesses. At the OWL joint stand (Hall 7, A12) over 40 exhibitors will demonstrate applications in the areas of machine diagnostics, predictive maintenance, process optimization, and robotics.
Prof. Dr. Roman Dumitrescu (Managing Director it’s OWL Clustermanagement GmbH and Director Fraunhofer IEM) explains: “Our research institutes are international leaders in the fields of machine learning, cognitive assistance systems and systems engineering. At our four universities and two Fraunhofer Institutes, 350 researchers are working on over 100 projects to make Artificial Intelligence usable for applications in industrial value creation. With it’s OWL, we bring this expert knowledge into practice. In 2020, we will launch three new strategic initiatives worth 50 million € to unlock the potential for AI in production, product development and the working world for small and medium-sized enterprises.”
In the initiative ‘AI Marketplace’ 20, research institutes and companies are developing a digital platform for Artificial Intelligence in product development. Providers, users, and experts can network and develop solutions on this platform. In the competence centre ‘AI in the working world of industrial SMEs’, 25 partners from industry and science make their knowledge of work structuring in the context of AI available to companies.
Learning machine diagnostics and ‘SmartBox’ for process optimization
The Institute for Industrial Information Technology at the OWL University of Applied Sciences and Arts will present new results for intelligent machine diagnostics at the trade fair. Using a three-phase motor, it will be illustrated how learning algorithms and information fusion can be used to reliably identify, predict, and visualize states of technical systems. Patterns and information hidden in time series signals are learned and presented to the user in an understandable way. Inaccuracies and uncertainties in individual sensors are solved by conflict-reducing information fusion. For example, motors can be used as sensors. Within a network of sensors and other data sources in production plants, motors can measure the “state of health” and analyze the causes of malfunctions via AI. This reduces scrap and saves up to 20 percent in materials.
The ‘SmartBox’ of the Fraunhofer Institute IOSB-INA is a universally applicable solution that identifies anomalies in processes in various production environments on the basis of PROFI-NET data. The solution requires no configuration and learns the process behavior.
With retrofitting solutions of the Fraunhofer Institute, companies can prepare machines and systems in their inventory for Industrie 4.0 applications without major investment expenditure. The spectrum ranges from mobile production data acquisition systems in suitcase format for studies of potential to permanently installable retrofit solutions. Intelligent sensor systems, cloud connections and machine learning methods build the basis for data analysis. This way, processes can be optimised and more transparency, control, planning, safety, and flexibility in production can be achieved.
Cognitive robotics and self-healing in autonomous systems
The Institute of Cognition and Robotics (CoR-Lab) presents a cognitive robotics system for highly flexible industrial production. The potential of model-driven software and system development for cognitive robotics is demonstrated by using the example of automated terminal assembly in switch cabinet construction. For this purpose, machine learning methods for environ- mental perception and object recognition, automated planning algorithms and model-based motion control are integrated into a robotic system. The cell operator is thereby enabled to perform different assembly tasks using reusable and combinable task blocks.
The research project “AI for Autonomous Systems” of the Software Innovation Campus Paderborn aims at achieving self-healing properties of autonomous technical systems based on the principles of natural immune systems. For this purpose, anomalies must be detected at runtime and the underlying causes must be independently diagnosed. Based on the localization it is necessary to plan and implement behavioral adjustments to restore the function. In addition, the security of the systems must be guaranteed at all times and system reliability must be increased. This requires a combination of methods of artificial intelligence, machine learning and biologically inspired algorithms.
Predictive maintenance and digital twin
Within the framework of the ‘BOOST 4.0’ project, the largest European initiative for Big Data in industry, it’s OWL is working with 50 partners from 16 countries on various application scenarios for Big Data in production. it’s OWL focuses on predictive maintenance: thanks to the systematic collection and evaluation of machine data from a hydraulic press and a material conveyor system, it is possible to identify patterns in the production process in a pilot company. The Fraunhofer IEM has provided the technological and methodological basis. And successfully so: over the past two years the prediction of machine failures has been significantly improved in this specific application by means of machine learning methods. The Mean Time To Repair (MTTR) has already been reduced by more than 30 percent. The Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) is now six times longer than before. A model of the predictive production line can be seen at the stand.
The digital twin is an important prerequisite for increasing the potential for efficiency and productivity in all phases of the machine life cycle. Companies and research institutes are working on the technical infrastructure for digital twins in an it’s OWL project. Digital descriptions and sub-models of machines, products and equipment as well as their interaction over the entire life cycle are now accessible thanks to interoperability. Requirements from the fields of energy and production technology as well as existing Industrie 4.0 standards and IT systems are taken into account. This is expected to result in potential savings of over 50 percent. At the joint stand, Lenze and Phoenix Contact will use typical machine modules to demonstrate how digital twins can be used to exchange information between components, machines, visualisations and digital services across manufacturers. Interoperability proves for the first time how the combination of data can be used to create useful information with added value for different user groups. For example, machine operators and maintenance staff can detect anomalies and receive instructions for troubleshooting.
Connect and get started – production optimization made easy
The cooperation in the Leading-Edge Cluster gives rise to new business ideas that are developed into successful start-ups. For example, Prodaso—a spin-off from Bielefeld University of Applied Sciences—has developed a simple and quickly implementable solution for the acquisition and visualization of machine and production data. The hardware can be connected to a machine in a few minutes via plug-and-play. The machine data is displayed directly in the cloud.
Prodaso has succeeded in solving a central challenge: Until now, networking machines from different manufacturers have been complex and costly. The Prodaso system can be retrofitted to all existing systems, independent of manufacturer and interface. In addition, the start- up also provides automated analysis and optimization tools. This enables companies to detect irregularities and deviations in the process flow at an early stage and to initiate appropriate measures. The company, founded in 2019, has already connected approximately 100 machines at companies in the manufacturing industry.

by Gary Mintchell | Dec 6, 2016 | Automation, Process Control, Workforce
The war is over and we have won. The war of handheld communication devices loose in the wilds of a plant, that is. Remember only a few years ago–like maybe two–when there was much angst in the media (except from me) about bringing handheld mobile communication into the plant? Now vendors are tripping all over themselves bringing out cool new toys to help maintenance, operations, and engineering do their jobs.
Here is a new tool from ABB. ABB has taken the next step with its Field Information Manager – the first FDI based Device Management tool in the market, with the introduction of its Field Information Manager 1.1 Handheld Edition. This easy-to-use software is now available for sale. The Handheld Edition makes it possible for the user to do configuration, parametrization and diagnosis of the HART instruments in many locations – in the field, at the back of the panel / junction box or in the instrumentation laboratory.
The Field Information Manager is designed to help users be more efficient in the configuration and management of their smart devices. Users do not need to invest in proprietary handheld terminal hardware; this eliminates the extra expense of proprietary hardware and significantly reduces lifecycle maintenance costs. The Field Information Manager can be installed on any Windows tablet / laptop / computer, thereby multiple instrumentation programs can be installed on a single machine. It is very quick to install and saves time for instrument and service technicians. Users can get started in less than three minutes, and can download all needed packages and files at www.abb.com/fieldinfo at any time.
Production technology vendors are really getting wise to the modern world about online stores. Field Information Manager Store and Print device configuration allows easy transfer of parameters from one device to another and eliminates manual recording of parameters.
Other key features of the Field Information Manager Handheld Edition include: Interoperability based on FDI components Online and offline parametrization Documentation of parameters and settings Novel concepts for ease of use and navigation with touch support ABB instrumentation FDI Device Packages ready to download Generic HART Device Package for all HART devices Supports installed base – DD/EDD files Visit www.abb.com/fieldinfo to learn more.

by Gary Mintchell | Jan 5, 2016 | Automation, News, Process Control, Technology
Just catching up on news that has built up over the extended holidays from Thanksgiving through New Years with one on process automation. I had a chat with Control Station’s Dennis Nash about the planned integration of its PlantESP Loop Performance Monitoring technology within the PlantPAx distributed control system from Rockwell Automation. Process data will be accessed natively from within the PlantPAx system environment using FactoryTalk Historian, and individual PID control loop configuration will be automatically populated to the new application’s dashboard.
Rockwell just keeps growing its process business. Its Process Systems User Group held last November in Chicago was yet another large gathering.
“Rockwell Automation continues its efforts to better serve the process industries by leveraging best-in-class solutions from its network of Encompass partners,” shared Tim Shope, Global Process Technical Consultant Manager from Rockwell Automation. “PlantESP is an obvious fit in that it will provide our customers with enhanced awareness of issues affecting their process’ day-to-day operational efficiency.”
Control Station’s PlantESP actively monitors the performance of PID control loops on a plant-wide basis and provides actionable insights. Equipped with a portfolio of key performance indices and advanced forensic tools, PlantESP simplifies the identification of performance issues and the isolation of the associated root-causes. Specific performance challenges addressed by PlantESP range from mechanical and controller tuning issues to constraints associated with process architecture. PlantESP uses a production facility’s existing process data and proactively alerts production staff of negative performance trends.
“The average plant has 100s if not 1000s of control loops which can be challenging for production staff to manage,” noted Rick Bontatibus, Control Station’s Vice President of Global Sales. “The combination of the PlantPAx System and PlantESP enables those same staff to focus their efforts on issues that will have the greatest impact on production efficiency and throughput.”
PlantESP is recognized as a leading control loop performance monitoring technology that has been successfully deployed at production facilities spanning the process industries. It is equipped with an array of highly effective and proprietary diagnostic tools, including advanced KPIs for identifying and quantifying stiction – a leading mechanical issue facing process engineers. PlantESP also includes a unique optimization utility called TuneVue that proactively captures everyday output changes for the purpose of isolating control loops that are in need of tuning. TuneVue is based on Control Station’s NSS Modeling Innovation and it is the only such utility that can accurately model the noisy, oscillatory process dynamics which are typical of industrial production and control environments. Collectively these and other PlantESP capabilities allow production staff to prioritize their efforts on issues that will have the greatest impact on performance.

by Gary Mintchell | Dec 1, 2015 | Automation, Technology
I have been writing on notifications in a personal sense. Here is an application of predictive notifications in manufacturing/production industry from ABB.
A new white paper that shows how predictive maintenance and notification technology can be combined to enable services that predict events that affect production, and then accelerate actions to avoid or exploit the events in order to produce higher equipment availability, more stable process performance and better product quality.

The white paper, entitled, “Are You on Track? How Predictive Notification Keeps Production on Track,” notes that though notifications are all around us (think smart phones with notifications for appointments, social media, software updates, sports scores, stock prices etc.), they haven’t yet entered the realm of industrial production. The paper proposes that the reason is because most notifications tell what has already happened. But combining notification technology with predictive maintenance technology can create a solution in which notifications become part of the daily industrial plant work practice.
“We have long provided control technology that triggers alarms for certain scenarios,” said Dan Duncan, Vice President, Sales and Operations for ABB Process Automation Service. “And we also deliver services that can automatically identify, categorize and prioritize maintenance issues that should be addressed. Both of these technological developments have made a huge impact on global industrial production.
“But what has been missing from our toolset is a simple way to take what is identified, categorized and prioritized by these advanced services technologies, and quickly and efficiently put an action into the hands of someone who can actually do something about it now,” Duncan said. “This white paper represents our thinking on how this can be accomplished by industrial producers everywhere.
“We expect it to have a significant beneficial effect on improving production efficiencies,” he said.
The paper covers predictive maintenance technology, problems with historical predictive approach and how to resolve those problems. The paper further identifies the value that can be produced by predictive notification technologies, and outlines a path to implementing a predictive notification program, including step-by-step guidance on how to get there.
by Gary Mintchell | Jan 5, 2015 | News
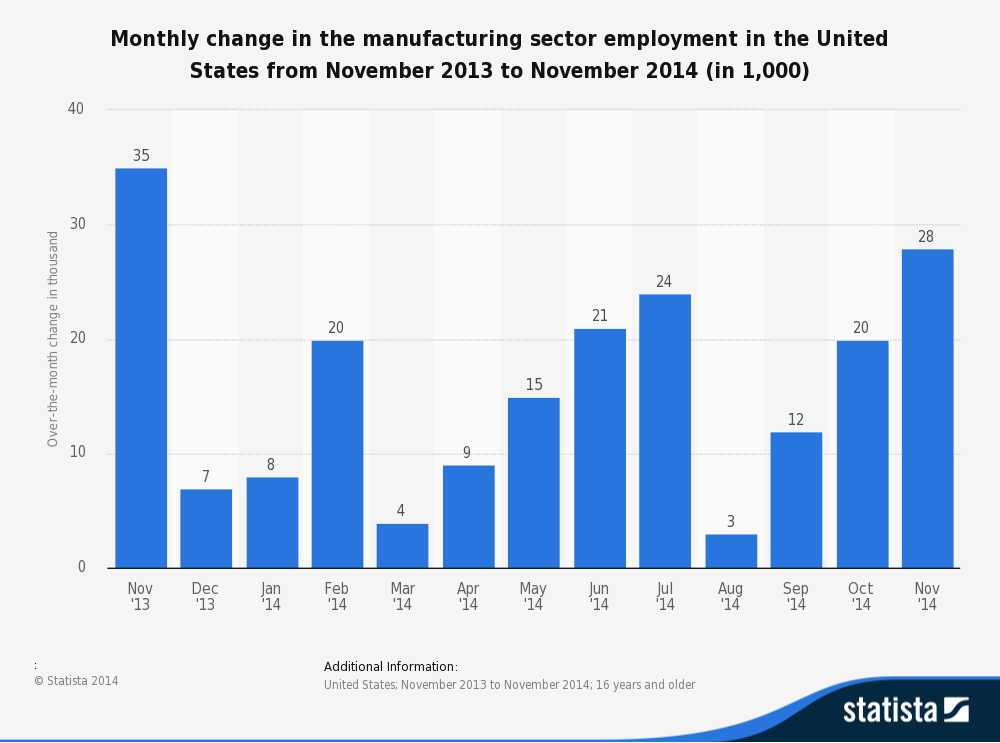
BLS Statistics
 This statistic from the US Bureau of Labor Statistics shows the monthly change in the manufacturing sector employment in the United States. The data are seasonally adjusted. According to the BLS, the data is derived from the Current Employment Statistics (CES) program which surveys each month about 140,000 businesses and government agencies, representing approximately 440,000 individual worksites, in order to provide detailed industry data on employment. In the goods-producing sector, manufacturing increased by 28,000 in November 2014.
This statistic from the US Bureau of Labor Statistics shows the monthly change in the manufacturing sector employment in the United States. The data are seasonally adjusted. According to the BLS, the data is derived from the Current Employment Statistics (CES) program which surveys each month about 140,000 businesses and government agencies, representing approximately 440,000 individual worksites, in order to provide detailed industry data on employment. In the goods-producing sector, manufacturing increased by 28,000 in November 2014.
The Fed
The news from the Federal Reserve was also good.
Industrial production increased 1.3 percent in November after edging up in October; output is now reported to have risen at a faster pace over the period from June through October than previously published. In November, manufacturing output increased 1.1 percent, with widespread gains among industries. The rise in factory output was well above its average monthly pace of 0.3 percent over the previous five months and was its largest gain since February. In November, the output of utilities jumped 5.1 percent, as weather that was colder than usual for the month boosted demand for heating. The index for mining decreased 0.1 percent. At 106.7 percent of its 2007 average, total industrial production in November was 5.2 percent above its year-earlier level. Capacity utilization for the industrial sector increased 0.8 percentage point in November to 80.1 percent, a rate equal to its long-run (1972–2013) average.
Manufacturing output rose 1.1 percent in November, and the rates of change for prior months are stronger than reported previously. Factory output is now estimated to have been above its late-2007 pre-recession peak in both October and November. In November, the indexes for both durables and nondurables increased more than 1 percent, and the output of every major industry group increased or remained unchanged. Among durable goods industries, the output of motor vehicles and parts jumped 5.1 percent as a result of an increase of 900,000 units at an annual rate in total motor vehicle assemblies. Miscellaneous manufacturing, wood products, and machinery each recorded gains exceeding 1 percent. Among nondurable goods industries, output advances of more than 2 percent were registered by petroleum and coal products and by apparel and leather. The indexes for food, beverage, and tobacco products and for plastics and rubber products both increased 1.4 percent.
The capacity utilization rate for manufacturing moved up 0.8 percentage point in November to 78.4 percent, a rate 0.3 percentage point below its long-run average. The operating rates for nondurable goods and durables goods increased, and the rate for other manufacturing (non-NAICS) remained unchanged. The utilization rate for mines fell 0.8 percentage point to 87.9 percent, while the rate for utilities increased 3.9 percentage points to 82.4 percent.









