
by Gary Mintchell | Oct 30, 2019 | Automation, Technology
Years ago I dabbled in machine vision integration. It was fun and creative. My customers and I did some pretty cool quality control applications. So I maintain a liking for the technology even though the price of the hardware plummeted and ease-of-use skyrocketed. So, I bring you this interesting news.
Honeywell is collaborating with Papertech to develop and market TotalVision, a connected, camera-based detection system for the flat sheet industries. The system enables customers to identify and resolve defects on the production line, improving quality and efficiency. The fully integrated total quality control solution is designed for flat sheet and film processes in which surface detection and production break monitoring capabilities are critical for competitive success. This new solution is designed for paper, pulp, tissue, board, extruded film, calendaring, lithium-ion battery, copper and aluminium foil producers.
Combining Honeywell’s ExperionMX technology with market-leading Papertech’s TotalVision defect detection and event capturing capabilities, the solution provides a single-window operating environment for all aspects of process and quality control. Customers benefit from faster root cause determination of runnability and quality problems, thereby saving significant time in lost or downgraded production. When integrated with connected offerings such as Honeywell QCS 4.0, system data and analytics can be accessed anytime, anywhere, from any device.
“Honeywell represents an ideal collaborator for Papertech as our industry-leading WebInspector WIS and our WebVision web monitoring system (WMS) single platform TotalVision camera system seamlessly integrate with Honeywell’s quality control systems for a range of industries,” said Kari Hilden, CEO of Papertech Inc. “We look forward to working with the global Honeywell team and their customers.”
Honeywell will continue to support existing camera system users with parts and services, while offering an easy migration path to the new solution. Given the collaborative nature of the agreement, customers can choose to take a single party, single-window approach or to engage with Honeywell and Papertech separately.
“As the world moves from plastic to biomaterial-based packaging, and from hydrocarbon-based transportation to electric vehicles, flat sheet producers are under increased pressure to ensure output consistently meets a variety of performance and safety requirements,” said Michael Kennelly, global business leader for sheet, film and foil industries, Honeywell Process Solutions. “By bringing together Honeywell’s core strengths of measurement, control, connected applications and services in flat sheet production with Papertech’s leadership in web monitoring and inspection systems, we uniquely provide customers with that capability along with industry-beating lifecycle costs.”
Papertech is the global industry-leading machine vision system supplier for a range of web-based production lines with more than 1200 TotalVision installations in 42 countries. It is part of the IBS Paper Performance Group, a company with a more than 50-year history in delivering papermakers a full range of proven machine efficiency and product quality optimization solutions.
For more information visit Honeywell Quality Control Systems and Papertech TotalVision solutions.

by Gary Mintchell | May 29, 2018 | Internet of Things, News, Software, Technology
NI Week was last week, and for only the second time in 20 years, I didn’t go. NI, formerly National Instruments, has been focusing more on test and measurement lately. Not so much automation. My interest is mostly on its IoT efforts especially TSN. I figure I can get an interview with Todd Walter or whomever without the expense of a conference.
NI’s core competency lies as the provider of a software-defined platform that helps accelerate the development and performance of automated test and automated measurement systems. At NI Week it announced the release of LabVIEW 2018.
Applications that impact our daily lives are increasing in complexity due to the rapid innovation brought on by industry trends such as 5G, the Industrial Internet of Things, and autonomous vehicles. Consequently, the challenge of testing these devices to ensure reliability, quality and safety introduce new demands and test configurations, with decreased time and budget. Engineers need better tools to organize, develop and integrate systems so they can accomplish their goals within the acceptable boundaries.
Engineers can use LabVIEW 2018 to address a multitude of these challenges. They can integrate more third-party IP from tools like Python to make the most of the strengths of each package or existing IP from their stakeholders. Test engineers can use new functionality in LabVIEW 2018 to strengthen code reliability by automating the building and execution of software through integration with open interface tools like Jenkins for continuous delivery. Capabilities like this empower test engineers to focus on system integration and development where they can offer unique differentiation, rather than get bogged down in the semantics of how to use software tools or move IP from one to another. For test engineers using FPGAs for high-performance processing, new deep learning functions and improved floating-point operations can reduce time to market.
“NI’s continued commitment to its software-centric platform accelerates my productivity so I can focus on the challenges that yield the highest ROIs,” says Chris Cilino, LabVIEW framework architect at Cirrus Logic. “LabVIEW continues to minimize the effort of adding tests and code modifications to our validation framework, delivering a consistent process to maintain our software and incorporate the reuse of valuable IP without rewrites.”
To meet demands like testing higher complexity DUTs and shorter timeframes, engineers need tools tailored to their needs that they can efficiently use through their workflow, helping them to meet their exact application requirements. LabVIEW 2018 is the latest addition to NI’s software-centric platform that features products tailored to needs within distinct stages of their workflow – products that have been adopted in whole or in part by more than 300,000 active users.
With InstrumentStudio software providing an interactive multi-instrument experience, TestStand test management software handling overall execution and reporting and SystemLink software managing assets and software deployments, this workflow improves the productivity of test and validation labs across many industries. Each piece of the workflow is also interoperable with third-party software to maximize code and IP reuse and draws on the LabVIEW Tools Network ecosystem of add-ons and tools for more application-specific requirements.
Engineers can access both LabVIEW 2018 and LabVIEW NXG with a single purchase of LabVIEW.
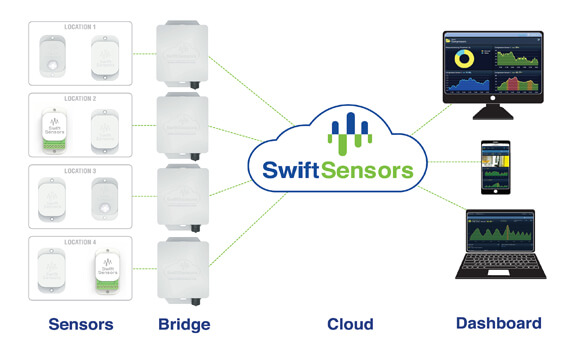
by Gary Mintchell | Mar 27, 2018 | Automation, Internet of Things, Wireless
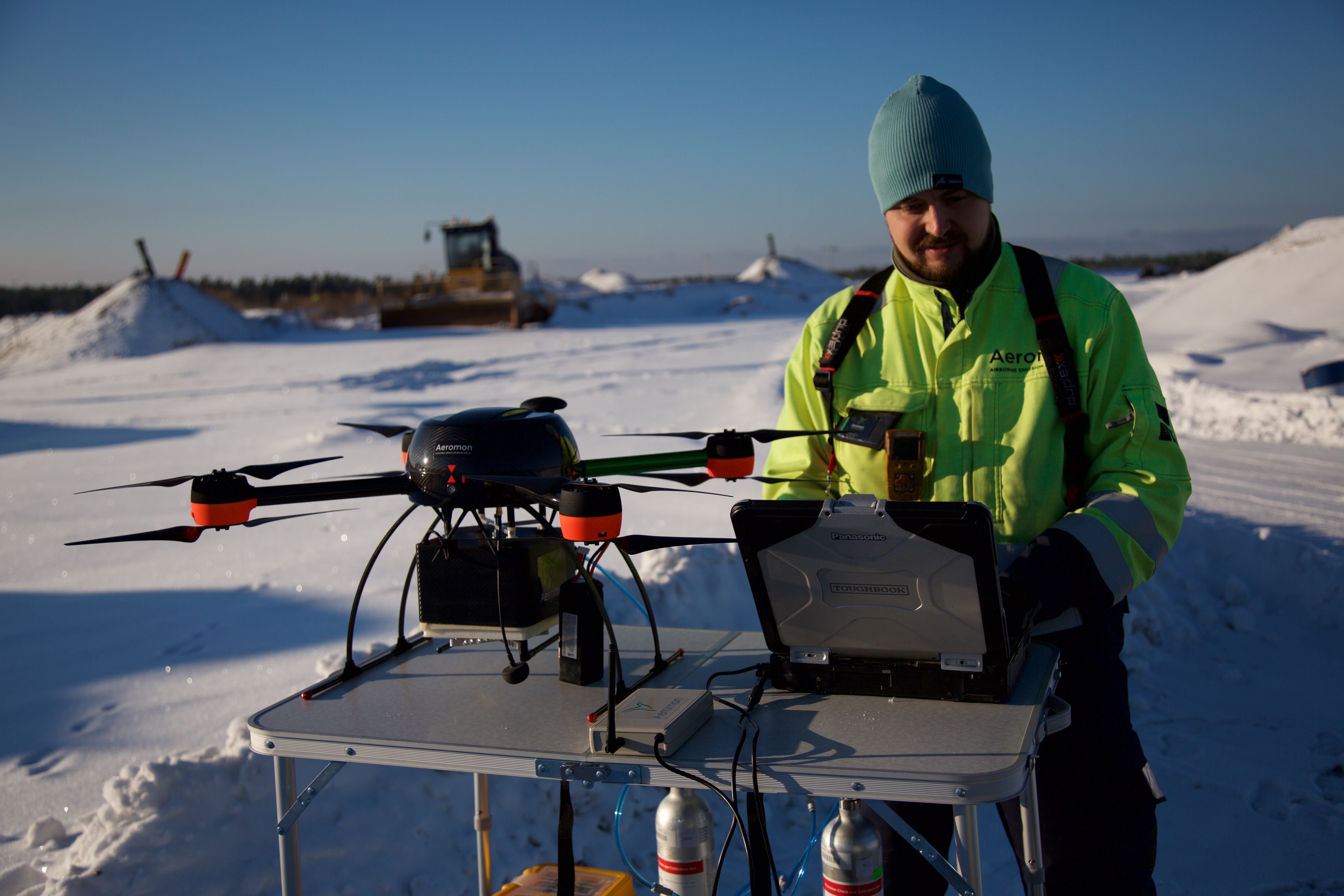

by Gary Mintchell | Mar 10, 2017 | Internet of Things, Operations Management, Technology
 Chris Anderson, while still editor-in-chief of Wired magazine, talked to a small group of us once about his fascination with drones. He got so involved he quit his job to start a company. Of course, in my day (ancient though it was), we called the RC (or radio controlled) model airplanes.
Chris Anderson, while still editor-in-chief of Wired magazine, talked to a small group of us once about his fascination with drones. He got so involved he quit his job to start a company. Of course, in my day (ancient though it was), we called the RC (or radio controlled) model airplanes.
The technology has developed so quickly that I’ve been amazed there have not been more industrial drone applications. Other than spying, which I’m sure goes on but we don’t talk about.
Aeromon, a Finnish cleantech startup that utilizes its innovative analytics platform and mobile sensors to flexibly map emissions in real-time, successfully demonstrated the effectiveness of drone-mounted platforms for measuring industrial emissions.
Drone Pilot Program
 A pilot program at the Ämmässuo waste treatment centre (operated by the Helsinki Region Environmental Services Authority HSY, Finland) compared historical data captured using hand-held measurement tools with aerial measurements taken by a remotely piloted aircraft (RPA) fitted with Aeromon’s sensor package. The composition and concentration of the biowaste stack and treatment facility emissions were also studied.
A pilot program at the Ämmässuo waste treatment centre (operated by the Helsinki Region Environmental Services Authority HSY, Finland) compared historical data captured using hand-held measurement tools with aerial measurements taken by a remotely piloted aircraft (RPA) fitted with Aeromon’s sensor package. The composition and concentration of the biowaste stack and treatment facility emissions were also studied.
 The resulting readings closely corresponded with HSY reference results, demonstrating the suitability of Aeromon’s aerial measurement platform for detecting fugitive emissions in a wide range of industrial settings, including those in which measurements may have previously been difficult to obtain.
The resulting readings closely corresponded with HSY reference results, demonstrating the suitability of Aeromon’s aerial measurement platform for detecting fugitive emissions in a wide range of industrial settings, including those in which measurements may have previously been difficult to obtain.
“When aerially-deployed, our sensor package can create a detailed emissions map of an industrial area. This data can be combined with environmental data in our cloud-based analytics platform Aeromon Cloud Service to provide a complete view of the emissions ,” says Jouko Salo, Chairman of Aeromon.
 The agile, accessible nature of the Aeromon platform was appreciated by HSY in particular. “The analysers used in Aeromon’s quadcopter were very portable and seemed reliable. The graphs provided in Aeromon’s final report were informative and easy to understand. We found the results obtained by Aeromon’s quadcopter to be close to our own measurements,” said Roni Järvensivu, Site Environmental Engineer as HSY Ämmässuo.
The agile, accessible nature of the Aeromon platform was appreciated by HSY in particular. “The analysers used in Aeromon’s quadcopter were very portable and seemed reliable. The graphs provided in Aeromon’s final report were informative and easy to understand. We found the results obtained by Aeromon’s quadcopter to be close to our own measurements,” said Roni Järvensivu, Site Environmental Engineer as HSY Ämmässuo.
With the HSY pilot case proving the effectiveness of the Aeromon platform in a real-world industrial setting, Aeromon is well positioned to serve a wide range of industries. “With emissions monitoring legislation tightening across the globe, the need for reliable fugitive emissions detection solutions is increasing,” continues Jouko Salo.
Unlike traditional technologies, the Aeromon platform maps and identifies emissions with cost-effective, lightweight sensors that analyze a wide range of gases, augmented with exact location information and environmental conditions parameters. The ultra-lightweight nature of Aeromon’s analyzer platform means it can be deployed in fixed and hand-held configurations, and can be carried by any drone/RPAS/UAS capable of carrying a professional camera set.
by Gary Mintchell | Nov 21, 2016 | Automation, Motion Control
This post regarding magnetic encoders is not my typical news. I met with the company at Automation Fair a couple of weeks ago. It’s the newest thing I’ve heard in encoders in a while. Thought I’d pass it along for all you servo engineers and business development managers out there.
 POSITAL’s new family of kit encoders provide the manufacturers of servomotors and other machinery with rugged, accurate and cost-efficient tools for building rotary position measurements into their products. The new kit encoders are based on POSITAL’s self-contained magnetic rotary encoders. Now however, the core components of these instruments are available as separate assemblies that can be readily integrated into other products.
POSITAL’s new family of kit encoders provide the manufacturers of servomotors and other machinery with rugged, accurate and cost-efficient tools for building rotary position measurements into their products. The new kit encoders are based on POSITAL’s self-contained magnetic rotary encoders. Now however, the core components of these instruments are available as separate assemblies that can be readily integrated into other products.
The POSITAL kit encoder components offer a number of advantages over the rotation measuring devices that have traditionally been used with servomotors and rotating equipment. Compared to resolvers, they are more accurate and offer multi-turn measurement capabilities. They also provide digital outputs instead of the analog signals produced by resolvers. While POSITAL’s magnetic encoder technology provides slightly less precision than the best optical disk encoders, it is less costly, less vulnerable to contamination from oil or dust and more resistant to shock and vibration. POSITAL encoders also provide an all-electronic multi-turn absolute position measuring capability that evaluates the full absolute angular position, including the total number of shaft rotations. The rotation counter is powered by the company’s well-proven Wiegand-effect energy harvesting technology so that rotation counts are always accurate, even if the rotations occur when external power is unavailable. This system eliminates the need for backup batteries or for the geared optical disks used in some products.
 POSITAL magnetic kit encoders are easy to incorporate into normal manufacturing processes since they don’t require extra-precision, near-cleanroom assembly conditions. A built-in self-calibration capability can compensate for small sensor-to-shaft alignment errors. The electronic components, including Hall-effect sensors, a 32-bit microprocessor and the Wiegand-wire energy harvesting system, are packaged in a convenient 36 mm diameter, 24.2mm deep unit. For servomotors with magnetic brakes, a special magnetic shield has been developed to isolate the magnetic pickups of the measurement system from the external magnetic fields.
POSITAL magnetic kit encoders are easy to incorporate into normal manufacturing processes since they don’t require extra-precision, near-cleanroom assembly conditions. A built-in self-calibration capability can compensate for small sensor-to-shaft alignment errors. The electronic components, including Hall-effect sensors, a 32-bit microprocessor and the Wiegand-wire energy harvesting system, are packaged in a convenient 36 mm diameter, 24.2mm deep unit. For servomotors with magnetic brakes, a special magnetic shield has been developed to isolate the magnetic pickups of the measurement system from the external magnetic fields.
The resolution of the new POSITAL kit encoders is 17 bit, with an accuracy of better than + 0.1°. The operating temperature range is -40 to +105 °C. These devices are available with a variety of non-proprietary communications protocols, including BISS, SSI and RS485-based protocols.
POSITAL is a supplier of advanced industrial position sensors used in a wide variety of motion control and safety systems. The company is also an innovator in product design and manufacturing processes and a pioneer of Industry 4.0 (Industrial Internet of Things/IIoT), offering customers the benefits of built-to-order products combined with the price advantages of mass-production. POSITAL is a member of the international FRABA group, whose history dates back to 1918, when its predecessor, Franz Baumgartner elektrische Apparate GmbH, was established in Cologne, Germany to manufacture relays. Since then, the company has played a trendsetting role in the development of rotary encoders, inclinometers and other sensor products. POSITAL has a global reach with subsidiaries in Europe, North America and Asia – and sales and distribution partners around the world.





 Chris Anderson, while still editor-in-chief of Wired magazine, talked to a small group of us once about his fascination with drones. He got so involved he quit his job to start a company. Of course, in my day (ancient though it was), we called the RC (or radio controlled) model airplanes.
Chris Anderson, while still editor-in-chief of Wired magazine, talked to a small group of us once about his fascination with drones. He got so involved he quit his job to start a company. Of course, in my day (ancient though it was), we called the RC (or radio controlled) model airplanes. A pilot program at the
A pilot program at the  The resulting readings closely corresponded with HSY reference results, demonstrating the suitability of Aeromon’s aerial measurement platform for detecting fugitive emissions in a wide range of industrial settings, including those in which measurements may have previously been difficult to obtain.
The resulting readings closely corresponded with HSY reference results, demonstrating the suitability of Aeromon’s aerial measurement platform for detecting fugitive emissions in a wide range of industrial settings, including those in which measurements may have previously been difficult to obtain. The agile, accessible nature of the Aeromon platform was appreciated by HSY in particular. “The analysers used in Aeromon’s quadcopter were very portable and seemed reliable. The graphs provided in Aeromon’s final report were informative and easy to understand. We found the results obtained by Aeromon’s quadcopter to be close to our own measurements,” said Roni Järvensivu, Site Environmental Engineer as HSY Ämmässuo.
The agile, accessible nature of the Aeromon platform was appreciated by HSY in particular. “The analysers used in Aeromon’s quadcopter were very portable and seemed reliable. The graphs provided in Aeromon’s final report were informative and easy to understand. We found the results obtained by Aeromon’s quadcopter to be close to our own measurements,” said Roni Järvensivu, Site Environmental Engineer as HSY Ämmässuo.
 POSITAL’s
POSITAL’s POSITAL magnetic kit encoders are easy to incorporate into normal manufacturing processes since they don’t require extra-precision, near-cleanroom assembly conditions. A built-in self-calibration capability can compensate for small sensor-to-shaft alignment errors. The electronic components, including Hall-effect sensors, a 32-bit microprocessor and the Wiegand-wire energy harvesting system, are packaged in a convenient 36 mm diameter, 24.2mm deep unit. For servomotors with magnetic brakes, a special magnetic shield has been developed to isolate the magnetic pickups of the measurement system from the external magnetic fields.
POSITAL magnetic kit encoders are easy to incorporate into normal manufacturing processes since they don’t require extra-precision, near-cleanroom assembly conditions. A built-in self-calibration capability can compensate for small sensor-to-shaft alignment errors. The electronic components, including Hall-effect sensors, a 32-bit microprocessor and the Wiegand-wire energy harvesting system, are packaged in a convenient 36 mm diameter, 24.2mm deep unit. For servomotors with magnetic brakes, a special magnetic shield has been developed to isolate the magnetic pickups of the measurement system from the external magnetic fields.



