
by Gary Mintchell | Aug 20, 2018 | Internet of Things, Manufacturing IT, Operations Management
Siemens is serious about building out its IoT platform, Mindsphere, on it way to realizing the vision of the technology supplier of digital transformation in manufacturing. How else to describe the €0.6 billion (or about $700 million) acquisition of Mendix, a popular low-code application development platform.
Mendix, which was founded in the Netherlands but now has its headquarters in Boston, will continue to operate as usual and keep its name, but Siemens notes that it will also use the company’s technology to accelerate its own cloud, IoT and digital enterprise ambitions.
“As part of our digitalization strategy, Siemens continues to invest in software offerings for the Digital Enterprise. With the acquisition of Mendix, Siemens continues to add to its comprehensive Digital Enterprise and MindSphere IoT portfolio, with cloud domain expertise, cloud agnostic platform solutions and highly skilled people,” said Jan Mrosik, CEO of Siemens’ Digital Factory Division.
Mendix’s service is already deeply integrated into IBMs’, SAP’s and Pivotal‘s cloud services. Mendix co-founder and CEO Derek Roos notes that his company and Siemens first discussed a strategic partnership, but as those talks progressed, the two companies moved toward an acquisition instead. Roos argues that the two companies’ visions are quite similar and that Siemens is committed to helping accelerate Mendix’s growth, extend the company’s platform and combine it with Siemen’s existing MindSphere IoT system.
“If you’ve ever wondered which low-code platform will have the viability to invest and win in the long term, you no longer have to guess,” Roos writes. “This commitment and investment from Siemens will allow us to accelerate R&D and geo-expansion investments significantly. You’re going to see faster innovation, more reach and an even better customer experience from us.”
Over the course of the last few years, ‘low-code’ has become increasingly popular as more and more enterprises try to enable all of their employees to access and use the data they now store. Not every employee is going to learn how to program, though, so tools like Mendix, K2 and others now make it easy for non-developers to quickly built (mostly database-backed) applications. (See my last post on ERP and “consumerization”.)
Here is a longer explanation from Roos’ blog:
[https://www.mendix.com/blog/siemens-to-acquire-mendix/]
As the world around us gets increasingly connected, organizations are facing increasing challenges to cope with vast amounts of data and customers are increasingly expecting entirely new experiences and interactions. New technologies like VR, IoT and AI will drive an incredible convergence between the digital and physical worlds, creating entirely new industries and business moments in which people, data, businesses and things work together, dynamically.
This, once again, will put more pressure on business/IT organizations to adapt and change how apps are built and consumed, in ways that few can comprehend right now. And just like we’ve done for web and mobile applications, we also intend to set the direction and lead the market for our customers in this new era.
And this is where Siemens comes in.
As one of the world’s largest industrial powerhouses, there are few companies on the planet that are dealing more mission-critical data and better positioned to blur the lines between our physical and digital worlds. With millions of connected devices and systems, operations in more than 200 countries, and more than 15,000 software engineers, Siemens has access to know-how, expertise and reach few others can match. Even fewer software companies can attempt to compete with such scale in ‘things’.
Siemens has been on a mission to leverage its foothold and data-rich infrastructure in the physical world, to become a leader in the digital world, investing over $10B in the last decade to acquire and build out software businesses, and to create the Industrial IoT platform, MindSphere.
Our two teams first met over a year ago and what started as a discussion about a strategic partnership, gradually evolved into a much bigger vision. The more time we spent together, the more we realized how our visions were aligned. Together with Joe Kaeser, CEO Siemens AG, Jan Mrosik, CEO Digital Factory Division, and Tony Hemmelgarn, CEO PLM Software, we identified three strategic areas where we could win together:
- Accelerate Mendix’ leadership in low-code by doubling down on R&D investments and geographical expansion: By becoming a part of Siemens, we will be able to access an even bigger investment than going public, and we will immediately get access to an enormous global infrastructure that would take much longer to stand-up ourselves. We are committed to extending our leadership in low-code and will significantly accelerate investments in R&D, Customer Success and global expansion.
- Combine Mendix and MindSphere to create the digital operating system for the physical world: With billions of intelligent devices and machines connected to the cloud, organizations will require a new kind of platform to turn these massive amounts of data into real-time business value. By combining Mendix and MindSphere, we will be in a unique position to bridge the physical and digital worlds.
- Extend the Mendix platform to develop world-class and deeply integrated industry SaaS solutions: Becoming a part of Siemens gives us unprecedented access to deep industry know-how, network and expertise. Together with our partner ecosystem, we’ll be able to extend the Mendix platform with deeply integrated vertical solutions across a wide range of industries. Combining low-code with best-practice solutions and templates will provide even more value and speed to market for our customers.

by Gary Mintchell | Aug 18, 2018 | Asset Performance Management, Operations Management, Software
Who buys enterprise software applications, how and why? I ran across this article by a contact of mine, Gabriel Gheorghiu, Founder and principal analyst at Questions Consulting, with a background in business management and 15 years experience in enterprise software. I thought it would be most useful. I’m not an ERP analyst, but I have some background and training on the financial side of things. I think this analysis fits with other large-scale software acquisition projects, though, including MES/MOM, analytics, asset performance, and the like.
This will summarize some interesting points. I highly recommend reading the whole thing.
Before we begin, my brief take on enterprise software applications. How many of you have been involved with an SAP acquisition and roll out? How many happy people were there? Same with Oracle or any other ERP, CRM, MES, APM, etc. application. Why did using Microsoft Excel seem to go better?
Well, the big applications all force you to change all your business processes to fit their template. You build Excel to fit what you’re doing. It’s just not powerful enough to do everything, right?
Gheorghiu conducted interviews with 225 companies who were all looking for enterprise resource planning (ERP). The goal of this survey was simple – listen and learn from what these companies had to say about their individual decision-making strategies. We all agree that this is not a simple task. But we also agree that selecting the best ERP software is a critical factor for business success.
Here is why the research phase of this process is considered to be so vital:
- It has the greatest impact on all the subsequent phases and consequently, your final decision.
- Research begins at home – in other words, the first step is to determine your company’s specific and unique needs.
- Once your company has thought through and determined its software requirement, then and only then does the process to evaluate vendors and their offerings begin. This can be a very challenging step because many companies are not equipped with the time, knowledge, or tools to perform this step.
Buyer Profiles: Who’s Looking for ERP and Why?
One problem for analysis is that many are not doing business in just one industry. The breakdown of companies in our business sample, by industry, was as follows: manufacturing (47%), distribution (18%), services (12%), construction (4%), retail (3%), utilities (3%), government (3%), healthcare (3%), and other (10%). However, to complicate matters a little, 20% of manufacturers also manage distribution and some distributors include light manufacturing in their operations, like assembly.
“Companies looking to invest in business software may very well be addressing this additional challenge – looking for a comprehensive package that integrates all aspects of a business. ERP software systems are powerful and comprehensive but are not necessarily known for their agility and ability to accommodate many disparate functions.”
Gheorghiu identifies as a strong influencer consumerization, which changes focus from organization-oriented offerings to end-user focused products. “This was a highly significant turning point in the IT marketplace. By developing new technologies and models that originate in the consumer space rather than in the enterprise sector, software producers opened up the market to a flood of small and medium-sized businesses looking for more cost effective, and less complicated solutions to run their businesses.”
The consumerization of software (as noted above) has precipitated the move by many companies away from enterprise IT towards more streamlined and user friendly consumer-oriented technology. This change is equally relevant for ERP software and manufacturing companies have participated in this very significant development, albeit more cautiously and slowly than SMBs.
Most industries follow a “purposeful implementation” strategy, managing software adoption as a series of “sprints in a well-planned program” rather than insisting on the “all or nothing” approach.
For example, a small company looking to invest in software might decide to begin with an accounting system which can be used alongside point solutions and spreadsheets. As companies grow and their transactions become more complex, they may find that they have also outgrown their initial software selections.
The chart below provides a visual analysis of the mix of software that is currently utilized by our business sample:
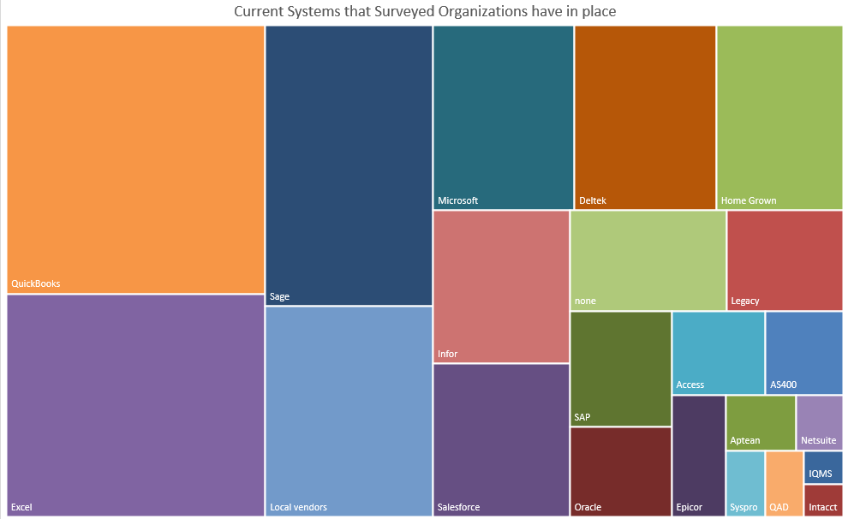
Some relevant comments we extracted from our survey included:
- The CEO of a small services company mentioned that he was “tired of the hodgepodge of systems”
- A manufacturer considered their current arrangement to be “very siloed.” Reconciling the inventory balance is a “constant battle.”
Buyer Behavior: How are Companies Approaching ERP Selection?
The selection process is most successful when companies adhere to some basic selection rules: involve as many direct stakeholders as possible and keep business priorities and strategies firmly in mind when making the final decision.
Feature Functions
A software change can trigger a vast administrative upheaval within the company. It is important to carefully analyze the business case for the change and whether it supports the level of disruption as well as the implementation time and spending that will be required. Even if the change may be entirely justified, a well thought out analysis is well worth the time and effort.
The Vendors in the Spotlight
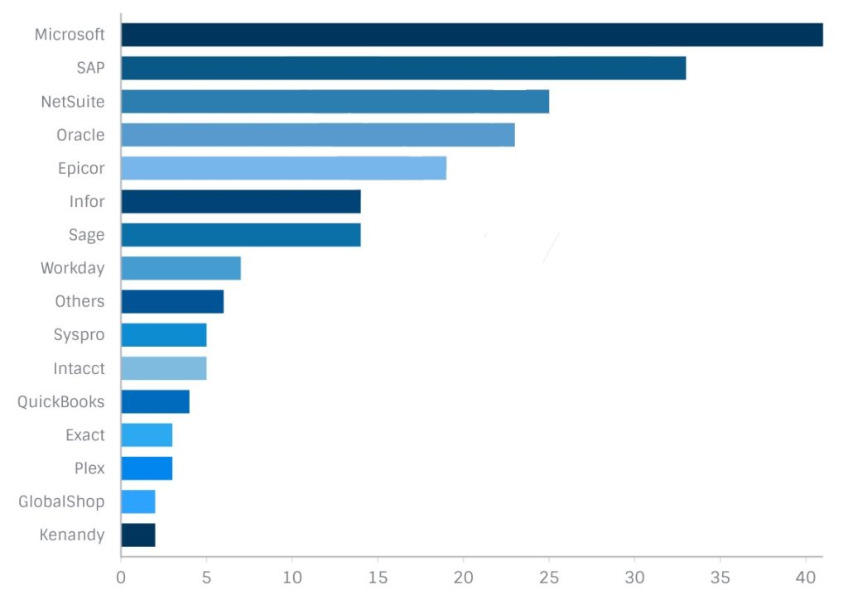
According to our survey results, the chart below identifies the vendors under consideration by the companies surveyed. A majority of companies (53%) were not, for the moment, looking at specific vendors. However 47% of respondents had narrowed their search to specific vendors.
Who’s Involved in this Decision Selection Process?
Our sample results indicate that the people in charge of the selection process are distributed as follows: employees in the finance and accounting departments (23%), IT department employees (23%). The other important categories were independent consultants helping companies with the selection process (17%), operations managers (17%) and presidents or CEOs (12%). It is worthwhile mentioning that project managers and business analysts only made up 5% of the total.
By far, the most effective method of choosing a software is to employ a collaborative system whereby the actual stakeholders of that system (the end-users) have a direct voice in the decision outcome. As the front-line users of the system, their insight and knowledge is very valuable. Their input along with all the other stakeholders input will produce the best possible outcome of this process.
An ERP system is a major business investment and is best handled with the appropriate amount of time and diligence given to the process.
The advent of cloud computing has indeed radically changed the landscape for deployment of business software. According to a recent press release by Gartner, “by 2020, a Corporate “No-Cloud” policy will be as rare as a “No-Internet” policy is today”. In other words, cloud deployment will become the default by 2020.
Our survey results, in fact, support Gartner’s analysis. Ninety-five percent of companies responded that they were open to a cloud deployment model, while just over 50% were willing to also consider on premises ERP. Of this latter group of respondents, 65% of them were manufacturers and distributors. This makes sense of course, given that these industries made significant investments in hardware and IT personnel and may not be as ready or as willing to move to the cloud model.
As for the preference for cloud computing (as demonstrated by our responses), we argue that it reflects the very strong tendency in the market to opt for simpler, more streamlined and less expensive computing solutions. As more information and assurances of security and stability by cloud providers enter the marketplace, more and more businesses will be convinced that the many benefits of the cloud outweigh some of their remaining concerns. Gartner’s prediction that cloud will increasingly be the default option for software deployment looks to be right on course.
Conclusion
An important consideration for companies embarking on an ERP software selection process – the average lifespan of an ERP system is approximately 5 to 10 years. If we consider important factors like the investment of capital, time, and loss of productivity that the selection and replacement of an ERP system requires, perhaps all companies would be more willing to invest the necessary effort in this process.

by Gary Mintchell | Aug 16, 2018 | Data Management, Internet of Things, Operations Management
The CEO of Zededa told me in an interview a few months ago that his mission was no less than to build the largest computing company on Earth without owning infrastructure. Its vision—create a new edge economy that allows applications to run anywhere.
When I wrote in April, the company was emerging from stealth mode. Its most recent announcement proclaims:
- First demonstrable cloud-native platform for edge applications, early customer access to end-to-end app operations platform purpose built for the edge underway
- Zero-touch infrastructure modernization for legacy embedded systems; simple to move legacy apps and OS from outdated systems to newer, cloud-native edge hardware
- Zededa joins EdgeX Foundry to bolster the organization’s vision of an open and secure cloud-native future that enables all new IoT applications
- Major edge system vendors turning to Zededa for operational automation, insights and protection of applications running on their systems
Zededa announced early access to its platform that provides real-time apps a simple “on-ramp” to the cloud-native edge. From legacy embedded systems to modern, AI-based IoT apps, the platform provides the scalability, security and visibility required to allow operations teams to unlock the power of real-time apps without concerns about bandwidth, latency or dependency on the cloud.
Operations technology teams have three primary situations to deal with when it comes to IoT applications: how to upgrade and secure a massive install base of legacy embedded systems, how to retrofit existing equipment with IoT sensors and applications to take advantage of real-time data, and how to deploy entirely new applications like AI-powered robots and self-driving fleets.
Closed, monolithic systems at the edge—either closed by design or closed because of legacy embedded device development workflows—are the last major impediment to solving these problems and enabling IoT to achieve its stated $1.3 trillion market potential. Zededa’s platform demonstrates how cloud-native edge solves the most urgent problem for organizations looking into digital transformation—upgrading and protecting legacy systems without truck-rolls—and gives solution providers a way to easily adopt IoT sensors and industrial gateways to provide real-time data to operational software. Initial natively-supported hardware partners include platforms built on ARM and Intel x86 processors from leading vendors including Advantech Corporation, Lanner, SuperMicro, and Scalys.
“Cloud-native edge computing will be a diverse universe unlike anything in cloud datacenters today,” said Roman Shaposhnik, VP of Product and Strategy at Zededa. “We are making the modernization of edge infrastructure secure, simple and automated in preparation for a fundamental shift away from legacy embedded systems. An open system that allows BYO hardware into a cloud-native platform is a start of the future: a computing environment that is distributed, autonomous and cooperative.”
To help drive entirely new applications and operational possibilities at the edge across a diverse universe of devices, Zededa has joined EdgeX Foundry, a vendor-neutral open source project hosted by The Linux Foundation with a goal to build a common open framework for IoT edge computing.
“Interoperability and convergence on common industry standards is vital for organizations deploying next-generation distributed computing solutions at the IoT Edge,” said Jason Shepherd, Chair of EdgeX Foundry Governing Board and Dell Technologies IoT CTO. “By joining EdgeX Foundry’s efforts Zededa will help promote the project’s important work of creating an open ecosystem of secure, interoperable edge applications that will change user experiences and drive the future of business.”
Currently providing early access to select customers, Zededa is accepting sign-ups for demonstrations and private briefings.
Founded in 2016, Zededa is pioneering a cloud-native approach to the deployment, management and security of real-time edge applications at hyperscale for solutions ranging from self-driving cars to industrial robots. Zededa is headquartered in Santa Clara, CA with engineering and market development teams based in India, UK, Germany and Korea.
EdgeX Foundry is an open source project hosted by The Linux Foundation building a common open framework for IoT edge computing and an ecosystem of interoperable components that unifies the marketplace and accelerates the deployment of IoT solutions. Designed to run on any hardware or operating system and with any combination of application environments, EdgeX enables developers to quickly create flexible IoT edge solutions that can easily adapt to changing business needs.

by Gary Mintchell | Aug 8, 2018 | Automation, Process Control, Technology
Foxboro and Triconex looks to be on the path to health under Schneider Electric. Its annual user conference is this week in San Antonio. I‘d love to be there, but personally more important is “grandparent duty” that I’m on this week. So, I had the opportunity to talk with Gary Freburger, leader of the group, and Peter Martin, VP of marketing, to get an update and view of what I’ll be missing.
Gary Freburger began with the market rebounding due to current oil pricing. Business is starting to get strong. IA product line has done well and the process business also did well going up 6% in the first half of the year. He’s expecting majority of growth over the next two years. Schneider Electric is still investing around EcoStruxure system. Foxboro is continuing on the path they discussed with us at the last user conference—how to get more value from control systems going from “necessary evil” to value add in the eyes of customer executives. The strategy is to turn data and connectivity into a business driver. The goal is enabling better decisions and improving profitability.
Freburger discussed cooperating with OPAF for a comprehensive strategy. Then he dropped in an interesting tidbit—cooperation with AVEVA. I’ve wondered about how AVEVA with the inclusion of previous Schneider Electric software would work with the Foxboro side of things. He told me they now have and end-to-end relationship to improve time to market. He noted as oil prices dropped customers thought “what can I afford to do?” Now, all have reset expectations. As oil prices rebound, they have not changed expectations. Some interesting applications and strategies include AVEVA auto populate control system, digital twin of facility, operations feedback our systems to AVEVA’s, then customer asset management upgrade works easier.
Martin discussed how Schneider is trying to change the question—from how to do control to how do we help customers solve problems that impact business? He pointed out that they’ve been doing digitization for years. What’s new is how to drive this new approach. 40 years ago controls was a solution-driven business; then with digitization the industry went from solutions to technology-driven. The times now require a need to flip flop. Solutions oriented but with today’s portfolios taking it to a much higher level. The speed of industrial business has increased—what was stable, e.g. cost of electricity—is stable no longer. The speed means IT world can’t keep up. Built-in real-time accounting control helps plants go beyond control to profitability. Foxboro is still dedicated to taking the use of technology to the next level.
During the conference (while I am writing from the forests in southern Ohio while the grandkids are in bed), Schneider Electric announced the release of EcoStruxure Foxboro DCS Control Software 7.1.With expanded capabilities and an enhanced HMI, the updated software simplifies engineering and enhances the user experience, while expanding the ability of EcoStruxure Foxboro DCS to drive measurable operational profitability improvements, safely.
The EcoStruxure Foxboro DCS is an open, interoperable and future-proof process automation system that provides highly accurate and effective control over a manufacturing plant’s operational profitability. It is the only process control system that provides measurable operational profitability improvements and a future-proof architecture, enabling a measurable 100 percent ROI in less than one year.
EcoStruxure is Schneider Electric’s open, interoperable, IoT-enabled system architecture and platform. This includes Connected Products, Edge Control, and Apps, Analytics and Services. EcoStruxure has been deployed in 480,000+ sites, with the support of 20,000+ system integrators and developers, connecting over 1.6 million assets under management through 40+ digital services.
EcoStruxure Foxboro DCS Control Software 7.1 runs on Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016, to provide maximum flexibility while ensuring robust cybersecurity. When planning upgrades, Schneider Electric customers can mix Windows XP, Windows 7 and Windows 10 on the same system, allowing flexibility in scheduling and timing for upgrades. Customers can upgrade individual sections of the plant in any order, at any pace, to best accommodate plant production schedules. With Microsoft support for Windows 7 due to end in 2020, transitioning to Windows 10 allows EcoStruxure Foxboro DCS customers to benefit from the strongest operating system with the most up-to-date cybersecurity features.
Among other new and updated features, the continuously current EcoStruxure Foxboro DCS Control Software 7.1 now includes:
• EcoStruxure Field Device Expert that improves efficiency, safety and profitability, while considerably reducing time for startup and restarts. It includes:
◦ Intelligent Commissioning Wizard, to reduce commissioning time up to 75 percent by automating HART device commissioning and documentation processes.
◦ Device Replacement Wizard to significantly reduce time and expertise to replace or commission HART devices, either individually or in bulk.
◦ Bundled HART DD library for increased security, faster device deployment, eradication of version mismatch and elimination of cybersecurity risks previously created by moving documents from the HART consortium web page into the system.
• New HMI Bulk Graphics Editor for increased operational efficiency and reliability by greatly reducing engineering hours and improving quality during testing. Use in major projects shows that replicating hundreds of displays with the new Bulk Graphics Editor saves months of man hours and improves quality by delivering highly predictable results. The Bulk Graphics Editor makes migrating from the classic FoxView HMI to the new Foxboro DCS Control HMI easier, requiring far fewer engineering hours, which reduces the time and cost to transition between technologies.
• Control Editors Activity Monitor for increased efficiency by improving communication, workflow and collaboration.
• Real-time asset health condition monitoring for increased reliability.
• Future-proof technology supporting the latest FTD 2.0 standard, which improves compatibility with digitized field devices from Schneider Electric and third-party vendors.
• New migration path, along with the new HMI Bulk Graphics Editor, simplifies the transition from existing FoxView HMI displays to the EcoStruxure Foxboro DCS Control Software 7.1 HMI platform for a continuously current and future-proof system. An upgrade migration path is available from previous Control Software Versions 5.x, 6.x and 7.0. After upgrading, users can tap into newer technologies that improve productivity, cybersecurity, efficiency and profitability.

by Gary Mintchell | Jul 25, 2018 | Automation, Technology
Collaborative describes the latest and most important trend in robots. Even if I was summarily dismissed when I asked that question of the CEO of a robotic arm company at an IT event, I stand by that analysis.
Lately Mobile Industrial Robots (MiR) news came to my attention. I’ve put off writing until I connected with Ed Mullen, US VP of Sales for this Danish company.
He told me that MiR designs and manufactures Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR) which are a bit like a quantum jump from the older Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) with which you may be familiar. Especially if you’re older, like me.
AGVs followed a path which was usually a wire laid in the floor. It followed its route around the facility. Cool, but not really very intelligent.
AMRs operate similar to modern autonomous technology using a 2D map of the facility and a location system plus laser scanning LIDAR. Tell it a place to go, and like a GPS it calculates the best route and directs the mobile robot to its destination—safely. I have actually interacted with one of the company’s earlier versions at a trade show where it continuously ran a route around the booth.
He tells me that the company is really more of a software company than hardware. The object is to take open source software and package it so that the customer has great flexibility for applications while usually going from unboxing to operations in under an hour.
Product news
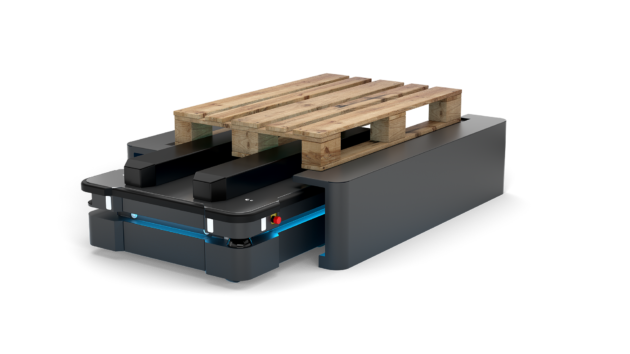
The latest product news is the launch of its MiR500 AMR. The robot has a lifting capacity of 500 kg (1102 lbs) and can automatically collect, transport and deliver pallets with speeds of nearly 4.5 miles per hour (mph). The MiR500 joins the MiR100 and MiR200 to form a complete fleet of flexible and easy-to-program MiR robots for both heavy and light transport that can optimize logistics throughout the entire production chain, from the warehouse to the delivery of goods.
“With the MiR500, we are extending the proven, strong technology and safety features that have made us the leading global supplier of autonomous mobile robots,” said Thomas Visti, CEO of Mobile Industrial Robots. “The MiR500 was developed to meet the needs of customers who have used our other robots and now see huge potential in the automation of the internal transport of heavy items and Euro-pallets. With MiR500, we’re setting new standards for how companies can use autonomous mobile robots.”
The user interface matches that used in the MiR100 and MiR200, which already optimize production processes in many of the world’s biggest multinational companies such as Airbus, Flex, Honeywell, Hitachi and Danone. The difference is the MiR500’s size, lifting capacity and areas of application.
“MiR500 is an extremely robust robot, so it’s perfect in industrial environments,” Visti said. “We’ve also incorporated the principles from the MiR100 and MiR200, where flexibility and user-friendliness are key attributes. This means that the MiR500 can be programmed without prior experience. It’s also simple to develop and replace top modules such as pallet lifters, conveyor belts and robot arms, so the robot can be used for different transport purposes.”
MiR has grown quickly since its founding in 2013, with sales rising by 500 percent from 2015 to 2016, and 300 percent from 2016 to 2017. With its second US office opening in San Diego this spring, and strong growth continuing worldwide, MiR expects to increase the number of employees from 65 to about 120 in 2018.
Acquisition
But wait, there’s more. Teradyne Inc. and the shareho6lders of Mobile Industrial Robots (MiR) announced the acquisition of privately held MiR of Odense, Denmark for €121 million ($148 million) net of cash acquired plus €101 million ($124 million at current exchange rate) if certain performance targets are met extending through 2020.
“We are excited to have MiR join Teradyne’s widening portfolio of advanced, intelligent, automation products,” said Mark Jagiela, President and CEO of Teradyne. “MiR is the market leader in the nascent, but fast growing market for collaborative autonomous mobile robots (AMRs). Like Universal Robots’ collaborative robots, MiR collaborative AMRs lower the barrier for both large and small enterprises to incrementally automate their operations without the need for specialty staff or a re-layout of their existing workflow. This, combined with a fast return on investment, opens a vast new automation market. Following the path proven with Universal Robots, we expect to leverage Teradyne’s global capabilities to expand MiR’s reach.”
MiR was profitable in 2017 with annual revenue of $12 million USD, more than triple 2016 revenues and had Q1’18 sales of $5 million.
“Joining Teradyne allows us to advance our engineering and development investments to provide greater value to our customers and further expand our market leadership in industrial autonomous mobile robots,” said Thomas Visti, CEO of MiR. “Teradyne’s worldwide reach, world-class engineering and support capabilities, financial strength and proven model for leveraging those strengths will help us grow in new and existing markets worldwide.”
“My main focus is to get our mobile robots out to the entire world,” said Niels Jul Jacobsen, CSO, founder of MiR. “With Teradyne as the owner, we will have strong backing to ensure MiR’s continued growth in the global market.”









