
by Gary Mintchell | May 24, 2019 | Software, Technology
I flew to Orlando May 22 as a guest of Siemens along with a select few other “influencers” to be introduced to a number of innovation projects fueled by Siemens technology. We met at the Dr. Phillips Center for Performing Arts in downtown Orlando (did you even know there was a downtown?), which itself is filled with Siemens equipment. There are few companies in the industrial area which I cover that have the vision and execution that Siemens is exhibiting right now.
By the way, there is a fantastic little taco place in downtown Orlando. Email or DM on Twitter, and I’ll share the name. Greg Hale of ISSSource.com and I had dinner there Wednesday. We agreed—among the best tacos we’ve had.
Barbara Humpton, CEO Siemens USA, led with an overview. Siemens has made a greater than $1B investment in R&D in the US with 7,000 engineers churning out 700 inventions per year.
She introduced former stunt man and motorcycle racer turned CEO Mike “Mouse” McCoy, CEO & Founder of HackRod. McCoy built on a foundation of Siemens PLM and SolidEdge CAD. He added a gaming engine. He was able to use VR for design reviews, interference checking, and simulation during the design process. We followed along with design and review of a new motorcycle. A few parts required somewhat exotic materials. Oak Ridge National Labs printed the parts from the design files downloaded from HackRod. The design teams were in Ventura, CA and Princeton, NJ with input from Munich, Germany. Collaboration was not a problem.
Beginning of design until component parts shipped to Orlando—2 weeks. The parts arrived Tuesday. McCoy and a partner assembled the motorcycle on Tuesday evening and wheeled (not drove) it onto the stage Wednesday about 1:30. Not bad? Heck, in my early career, we couldn’t have done a foam-core mock up in that time frame.
One thought McCoy left us with. “We need to talk STEAM, not just STEM—science, technology, engineering, arts, math.” It is now possible for artists and designers to be an intimate part of the team going from art to finished product quickly. 3D printing from PLM files. Way cool.
How about a high school mechanical design student given a project to provide a lighter prosthetic foot for an Army vet? Humpton introduced 18-year-old high school student Ashley Kimbel who had undertaken just such a project. She worked with the veteran to analyze his current “foot” looking for areas where weight could be eliminated. Then she had to learn how to fabricate and manufacture the device. We saw films of the veteran running with Ashley proving out the new prosthetic.
This is a long way from projects I had as a 17-year-old senior. Education and technology have come a long way in a lifetime. Oh, and her future? She wants to work in bioengineering designing and 3D printing organs. She will be working on that during her tenure at UAB. She is going to make a difference for many people.
I have many more ideas and conversations to capture. This will serve for now.
Check out #SiemensInnovates

by Gary Mintchell | Aug 20, 2018 | Automation, Technology
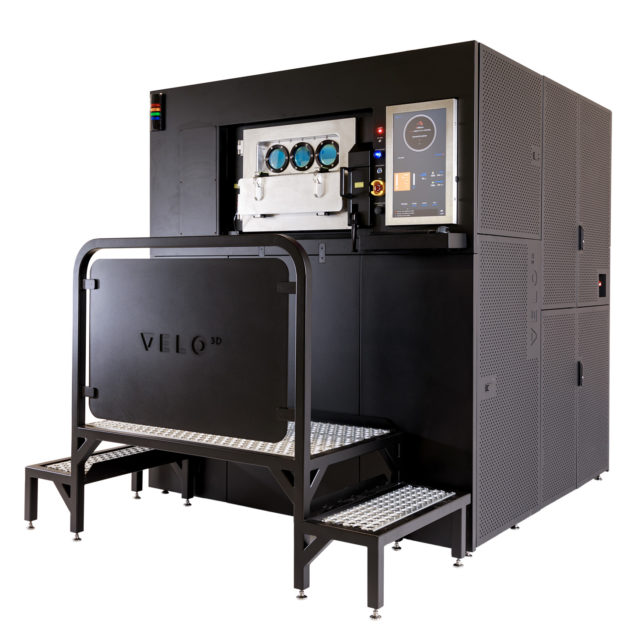
Moving additive manufacturing from plastics to metal and from hobbyist bench to the factory has attracted much attention. One of the problems with metal 3D printing (additive manufacturing) has been holding high tolerance for consistency. Velo3D today announced general release of its end-to-end metal additive manufacturing (AM) solution comprised of the Sapphire system, Flow print preparation software, and Intelligent Fusion technology. Together, the integrated solution solves some of the most difficult AM challenges including product design limitations, part-to-part consistency, process control and cost-effective manufacturing.

“Additive manufacturing has the potential to be revolutionary,” said Ashley Nichols, general manager at 3D Material Technologies (3DMT), a leading metal additive manufacturing services bureau. “Systems are getting bigger, but not delivering on the promises of metal additive manufacturing. Through a collaborative partnership, 3DMT and Velo3D are unlocking new applications, pushing the envelope of what is currently considered possible. We look forward to continued success, and to delivering on the promises of the potential of metal additive manufacturing.”
Sapphire System
The Sapphire system is a laser powder bed metal additive 3D printing system designed for high volume manufacturing. Sapphire is capable of building complex geometries including designs with overhangs that are less than five degrees and large inner diameters without supports – something previously unheard of in the AM industry. To deliver superior part-to-part consistency, Sapphire’s integrated in-situ process metrology enables first-of-its-kind closed loop melt pool control. To maximize productivity, the Sapphire system contains a module that enables automated change-over with offline unpacking.
Flow Print Preparation Software
Flow print preparation software includes support generation, process selection, slicing and simulation of complex part designs to validate execution feasibility before the build. Geometrical feature-driven processing enables low angles below five degrees. In addition, deformation correction technology enables the user to produce parts without the need for iterations, achieving a first print success rate of up to 90 percent. Flow minimizes the need for supports, reducing typical support volume by 3-5 times, which removes or reduces the laborious post processing necessary with conventional approaches.
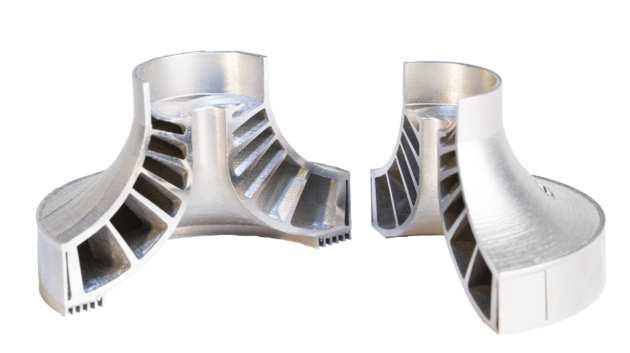
Intelligent Fusion Technology
Enabling an end-to-end integrated workflow, Intelligent Fusion is the technology that powers Flow software and the Sapphire system. Intelligent Fusion optimizes the AM process by combining thermal process simulation, print prediction, and closed-loop control during print execution.
“Four years ago, we set out with the bold vision of creating technology that could manufacture parts with any geometry to take additive manufacturing mainstream,” said Benny Buller, founder and CEO of Velo3D. “Our approach relies on creating deep insights in physics fundamentals, enabled by research, characterizing and understanding of core mechanisms, developing intelligent process control through software simulation and in-situ metrology. Today, Velo3D is working with some of the top OEMs and service bureaus creating parts that were once considered impossible.”
Velo3D systems are currently used by original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) and manufacturing service providers.
www.velo3D.com.

by Gary Mintchell | Mar 28, 2017 | Automation, Education, Leadership, Technology
Manufacturing in America—an event bringing together vendors, academia, end users of controls and automation. Siemens Industry, collaborating with its local distributor Electro-Matic, held a trade show/seminar series/thought leadership summit at the Marriott Renaissance Center Detroit March 22-23. The show has a distinct automotive industry feel, as you might expect, even though Detroit, and indeed all of Michigan, is reforming itself along high tech lines with less reliance on traditional automotive.
There was certainly a lot of thought leadership opportunity at the event. There was the Siemens Industry President of Digital Factory. There was the Governor of the State of Michigan.

And then, there was the group of high school students competing in the FIRST Robotics competition known as the ThunderChickens—Engineering A Better Way To Cross The Road. The picture shows a model of their robot. Such passion. Such creativity. The mechanical guy pointed to the control module. “It limits me to 6 motors,” he said. “Last year we only had one, but this year I could have used many more.”
Six motors!! What I’d have given as a kid building stuff to have one! Oh well, they were great.
 Raj Batra, President of Digital Factory for Siemens, said the focus is on digitalization. Digital Twin is a piece of digitalization. This is the digital representation of a physical thing—product, machine, or component. Siemens brought all this together through the 2007 investment in acquiring UGS to form Siemens PLM. “Companies thought it was hype back then, now we know it drives value,” said Batra. “If you are a pure automation company how do you accomplish all this without a design component? You can’t have the digital twin. Meanwhile, a CAE company that doesn’t have automation and control do manufacturing—what do you get?” Batra added challenging the competition.
Raj Batra, President of Digital Factory for Siemens, said the focus is on digitalization. Digital Twin is a piece of digitalization. This is the digital representation of a physical thing—product, machine, or component. Siemens brought all this together through the 2007 investment in acquiring UGS to form Siemens PLM. “Companies thought it was hype back then, now we know it drives value,” said Batra. “If you are a pure automation company how do you accomplish all this without a design component? You can’t have the digital twin. Meanwhile, a CAE company that doesn’t have automation and control do manufacturing—what do you get?” Batra added challenging the competition.
Batra continued, “We are close to a new era of autonomous manufacturing. And there is the growth of IIoT, we call Mindsphere. This all means manufacturing is no longer a black box to the enterprise. Indeed, it is strategic to the enterprise.”
Paul Maloche, vp sales and marketing Fori Automation, manufacturers of automated guided vehicles, discussed the methods by which collaboration with suppliers (in this case with Siemens) leads to innovation. Fori was diversifying from reliance on building machines for automotive applications, and evaluated the aerospace industry. The Siemens rep came in and said they could help get them into that market. But Fori would have to convert to Siemens control. The Fori team replied, “OK.” This led to development of automated guided vehicle technology and products. The partnership opened doors. Fori won several orders in aerospace market for the new AGVs with Siemens control.
 Alistair Orchard, Siemens PLM, riffing off a space movie, began his talk, “Detroit, we have a problem.” All the old business models of trying to ship jobs overseas has not worked. We need to make stuff to be successful as a society. “So much of what we do has not changed in 50 years in manufacturing,” he noted, “but digitalization can change everything. Additive manufacturing can lead to mass customization due to 3D printing using the digital twin. You can try things out, find problems in design or manufacturing. You can use predictive analytics at design stage. Digital enterprise is about manufacturing close to the customer.”
Alistair Orchard, Siemens PLM, riffing off a space movie, began his talk, “Detroit, we have a problem.” All the old business models of trying to ship jobs overseas has not worked. We need to make stuff to be successful as a society. “So much of what we do has not changed in 50 years in manufacturing,” he noted, “but digitalization can change everything. Additive manufacturing can lead to mass customization due to 3D printing using the digital twin. You can try things out, find problems in design or manufacturing. You can use predictive analytics at design stage. Digital enterprise is about manufacturing close to the customer.”
 Governor Rick Snyder, Michigan, touted his manufacturing background as former operations head at Gateway Computers. “As governor,” he said, “it’s about how you can build an ecosystem and platform for success. Long term, success needs talent. His philosophy contains the idea that we shouldn’t tell students what they should study, but let them know where opportunities are and how to prepare for them. The private sector needs to tell government what they need in the way of talent.”
Governor Rick Snyder, Michigan, touted his manufacturing background as former operations head at Gateway Computers. “As governor,” he said, “it’s about how you can build an ecosystem and platform for success. Long term, success needs talent. His philosophy contains the idea that we shouldn’t tell students what they should study, but let them know where opportunities are and how to prepare for them. The private sector needs to tell government what they need in the way of talent.”
Michigan has grown more manufacturing jobs than anywhere else in the country. Not only manufacturing, though, Michigan is also a center of industrial design. But the economy not only needs designers and engineers, but also people in skilled trades. “We need to promote that as a profession. We must break the silos that said your opportunities are limited to your initial career choice.”
Michigan has invested a lot in students, especially in FIRST Robotics, where Michigan teams have risen to the top. The state has also started a computer science competition in cyber security.
How are you innovating and making the world better?
 Josh Linkner, CEO Detroit Venture Partners, gave the keynote address on innovation. I’ll leave you with his Five Obsessions of Innovators.
Josh Linkner, CEO Detroit Venture Partners, gave the keynote address on innovation. I’ll leave you with his Five Obsessions of Innovators.
1. Curiosity—ask open ended questions
2. Crave what’s next—future orientation
3. Defy tradition—use Judo flip to turn idea on its head
4. Get scrappy—grit, determination, tenacity
5. Adapt fast

by Gary Mintchell | Apr 14, 2016 | Technology
 We all expect 3D Printing, also known as Additive Manufacturing, to be a disruptive. Or is it everyone who expects it? Will 3D Printing become the next technology to collapse layers in manufacturing just like the software and communications layers I’ve been discussing?
We all expect 3D Printing, also known as Additive Manufacturing, to be a disruptive. Or is it everyone who expects it? Will 3D Printing become the next technology to collapse layers in manufacturing just like the software and communications layers I’ve been discussing?
PwC just reported on its 2015 survey of manufacturers’ experiences and attitudes toward the technology. The results are somewhat mixed, as you would suspect given how new the technology is and how rapidly it is gaining acceptance.
PwC’s Robert McCutcheon posted a blog on LinkedIn introducing the latest results. I’m quoting the post here:
There are many different types of technology that are at the fingertips of manufacturers looking to become the next Factory of the Future. But there’s still that hesitation, there’s still the question: Is 3D printing (3DP) just hype?
According to PwC’s recent study, it’s not. In fact, it’s become quite clear that the technology, also known as additive manufacturing, is crossing from a period of experimentation to one of rapid maturation. Industrial 3D printers, once almost exclusively used for prototyping, are now on some of America’s factory floors and being rolled out on production lines.
How do we know?
Two years ago, PwC tested the waters to figure out to what extent U.S. manufacturers were adopting 3DP into their operations and how they expected the technology to play out in the future. In our latest report, we share what’s changed and the three most significant shifts that have emerged:
- More “doing,” less experimenting: Fewer manufacturers (17% versus 29% two years ago) are simply experimenting with 3DP to figure out how to use the technology. Now, just over half are using it for prototyping and final-products versus 35% two years ago.
- Greater expectations: Two years ago, just 38% of manufacturers expected 3DP to be used for high-volume production over the next 3-5 years. Now, 52% do. Interestingly, we saw a drop from 74% to 67% in the number of manufacturers that expect 3DP to be used for low-volume, specialized products.
- 3DP is still disrupting, though how it’s disrupting continues to evolve: Twenty-two percent say it will be disruptive to restructuring supply chains. The same percentage say it will threaten intellectual property.
Eighteen percent believe it will change relationship with customers. Two years ago, the primary concern was how it would disrupt the supply chain.
In “3D Printing comes of age in US industrial manufacturing“, we dive further into these three shifts and uncover sentiment from 2014 versus today. What’s clear is that the growth in 3DP and the range of ways it’s being implemented is demonstrating 3DP will be an important discussion to how manufacturers are assessing, shaping and expanding their businesses.
However, no matter where one is on the adoption scale, there are questions that must be addressed.

by Gary Mintchell | Jan 26, 2016 | Automation, Internet of Things, News, Operations Management, Technology
The PwC Industrial Manufacturing Trends 2016 post has been released. Check it out. There are some interesting ideas.
The authors Stephen Pillsbury and Robert Bono cite the painful lessons of recovering from 2001 and 2008 as leading to caution now displayed by manufacturing leaders. We’ve had a bit of an economic jolt. Where is it headed? The uncertainty leads to caution.
They reach an interesting conclusion, “Manufacturing may be facing some headwinds, but it’s undeniably in the midst of a technological renaissance that is transforming the look, systems, and processes of the modern factory. Despite the risks — and despite recent history — industrial manufacturing companies cannot afford to ignore these advances. By embracing them now, they can improve productivity in their own plants, compete against rivals, and maintain an edge with customers who are seeking their own gains from innovation.”
It is time, they say, to envision and prepare for a data-driven factory of the future.
They reveal four technology categories that are already driving much of the change. I’ll summarize. Check out the report for more depth. Most of these are not surprising, but they certainly must be factored in the thinking of manufacturing leaders.
Industrial Manufacturing Technologies
- Internet of Things (IoT): The connected factory is an idea that has been evolving for the past few years. Increasingly, it means expanding the power of the Web to link machines, sensors, computers, and humans in order to enable new levels of information monitoring, collection, processing, and analysis.
But for industrial manufacturing companies, the next generation of IoT technology should go well beyond real-time monitoring to connected information platforms that leverage data and advanced analytics to deliver higher-quality, more durable, and more reliable products.
Before investing in IoT, however, industrial manufacturing companies must determine precisely what data is most valuable to collect, as well as gauge the efficacy of the analytical structures that will be used to assess the data. In addition, next-generation equipment will require a next-generation mix of workers, which should include employees who can design and build IoT products as well as data scientists who can analyze output.
- Robotics: In many cases, robots are employed to complement rather than replace workers. This concept, known as “cobotics,” teams operators and machines in order to make complex parts of the assembly process faster, easier, and safer.Cobotics is rapidly gaining momentum, and successful implementations to date have focused largely on specific ergonomically challenging tasks within the aerospace and automotive industries. But these applications will expand as automation developers introduce more sophisticated sensors and more adaptable, highly functional robotic equipment that will let humans and machines interact deftly on the factory floor.
- Augmented reality: Recent advances in computer vision, computer science, information technology, and engineering have enabled manufacturers to deliver real-time information and guidance at the point of use.
- 3D printing: Also known as additive manufacturing, 3D printing technology produces solid objects from digital designs by building up multiple layers of plastic, resin, or other materials in a precisely determined shape.
The authors conclude with recommendations of how to consider necessary investments in these emerging technologies.






 Raj Batra, President of Digital Factory for Siemens, said the focus is on digitalization. Digital Twin is a piece of digitalization. This is the digital representation of a physical thing—product, machine, or component. Siemens brought all this together through the 2007 investment in acquiring UGS to form Siemens PLM. “Companies thought it was hype back then, now we know it drives value,” said Batra. “If you are a pure automation company how do you accomplish all this without a design component? You can’t have the digital twin. Meanwhile, a CAE company that doesn’t have automation and control do manufacturing—what do you get?” Batra added challenging the competition.
Raj Batra, President of Digital Factory for Siemens, said the focus is on digitalization. Digital Twin is a piece of digitalization. This is the digital representation of a physical thing—product, machine, or component. Siemens brought all this together through the 2007 investment in acquiring UGS to form Siemens PLM. “Companies thought it was hype back then, now we know it drives value,” said Batra. “If you are a pure automation company how do you accomplish all this without a design component? You can’t have the digital twin. Meanwhile, a CAE company that doesn’t have automation and control do manufacturing—what do you get?” Batra added challenging the competition. Alistair Orchard, Siemens PLM, riffing off a space movie, began his talk, “Detroit, we have a problem.” All the old business models of trying to ship jobs overseas has not worked. We need to make stuff to be successful as a society. “So much of what we do has not changed in 50 years in manufacturing,” he noted, “but digitalization can change everything. Additive manufacturing can lead to mass customization due to 3D printing using the digital twin. You can try things out, find problems in design or manufacturing. You can use predictive analytics at design stage. Digital enterprise is about manufacturing close to the customer.”
Alistair Orchard, Siemens PLM, riffing off a space movie, began his talk, “Detroit, we have a problem.” All the old business models of trying to ship jobs overseas has not worked. We need to make stuff to be successful as a society. “So much of what we do has not changed in 50 years in manufacturing,” he noted, “but digitalization can change everything. Additive manufacturing can lead to mass customization due to 3D printing using the digital twin. You can try things out, find problems in design or manufacturing. You can use predictive analytics at design stage. Digital enterprise is about manufacturing close to the customer.” Governor Rick Snyder, Michigan, touted his manufacturing background as former operations head at Gateway Computers. “As governor,” he said, “it’s about how you can build an ecosystem and platform for success. Long term, success needs talent. His philosophy contains the idea that we shouldn’t tell students what they should study, but let them know where opportunities are and how to prepare for them. The private sector needs to tell government what they need in the way of talent.”
Governor Rick Snyder, Michigan, touted his manufacturing background as former operations head at Gateway Computers. “As governor,” he said, “it’s about how you can build an ecosystem and platform for success. Long term, success needs talent. His philosophy contains the idea that we shouldn’t tell students what they should study, but let them know where opportunities are and how to prepare for them. The private sector needs to tell government what they need in the way of talent.” Josh Linkner, CEO Detroit Venture Partners, gave the keynote address on innovation. I’ll leave you with his Five Obsessions of Innovators.
Josh Linkner, CEO Detroit Venture Partners, gave the keynote address on innovation. I’ll leave you with his Five Obsessions of Innovators.
 We all expect 3D Printing, also known as Additive Manufacturing, to be a disruptive. Or is it everyone who expects it? Will 3D Printing become the next technology to collapse layers in manufacturing just like the software and communications layers I’ve been discussing?
We all expect 3D Printing, also known as Additive Manufacturing, to be a disruptive. Or is it everyone who expects it? Will 3D Printing become the next technology to collapse layers in manufacturing just like the software and communications layers I’ve been discussing?


