
by Gary Mintchell | Dec 6, 2019 | Internet of Things, Networking, Wireless
Suddenly the wireless networking side of IoT connectivity is hitting my radar. Since the culmination of the “wireless wars” of 10 years ago, this technology/market area has settled into supplying usable products. This information came from Honeywell—In short, by supplying ISA100 Wireless and WirelessHART connectivity to Cisco’s next-generation Wi-Fi Access Point, Honeywell’s OneWireless IoT Module can help users increase industrial plant productivity, worker safety, and digital transformation readiness.
Honeywell is developing a OneWireless IoT Module for the next-generation of Cisco’s industrial access points, the Cisco Catalyst IW6300 Heavy Duty Series Access Point. The Honeywell and Cisco technologies will form the backbone of Honeywell’s OneWireless Network.
The joint wireless solution enables Honeywell customers to quickly and easily deploy wireless technologies as an extension of their Experion Process Knowledge System (PKS). Combining the leading IT network technology by from Cisco and the leading Honeywell OneWireless multi-protocol technology provides customers with a single infrastructure that meets all their industrial wireless needs.
“For the past decade, Cisco and Honeywell have worked together to deliver secure, wireless solutions to connect mobile workers and field instrumentation in the most challenging process manufacturing environments,” said Liz Centoni, senior vice president and general manager, Cisco IoT. “We’ve had great success in bringing IT and operational teams together to reduce complexity and improve efficiency. Now, we are building on that foundation to extend the power of intent-based networking to the IoT edge.”
When combined with the Honeywell OneWireless IoT Module, the Cisco Catalyst IW6300 Heavy Duty Series Access Point offers the security, speed, and network performance needed to allow the seamless extension of the process control network into the field.
“The OneWireless IoT Module is Honeywell’s latest innovation as a leader in wireless technology,” said Diederik Mols, business director Industrial Wireless, Honeywell Process Solutions. “Our customers will benefit from OneWireless functioning as a seamless extension of Experion PKS and simplified deployment made possible by integrating the IoT module and aerials into a single unit.”

by Gary Mintchell | Aug 15, 2019 | News, Organizations
Here is a little bit of merger and acquisition activity of interest. One involving industrial cybersecurity; the other IT-oriented. Owl Cyber Defense and Tresys are coming together. I have been anticipating some consolidation in that space. Lots of startups. Can’t be that much business. In the other Dell Technologies appears to be rationalizing its organizational and investing complexity.
Tresys and Owl Cyber Defense to merge
Tresys Technology was recently acquired by DC Capital Partners, a private equity firm, and placed in a common holding company with Owl Cyber Defense. “The intention is to merge the two companies in the coming months, creating what we believe is the number one boundary security product and services company in the world. To both of us, nothing makes more strategic sense than this combination, and with DC Capital’s support we will be exploring additional strategic acquisitions to broaden our investment in innovation, geographies, and vertical markets. While we will continue to operate as separate businesses in the short term, over the coming months we will work on merging all operations and we will keep you fully apprised of those changes.”
Further from the message I received, “What does this mean for you? Both companies are fully committed to customer service excellence. You will continue to have access to our industry leading expertise in technology services and support; to help you select, configure, customize, maintain, and accredit solutions for any network separation issue. With our new ownership, there is a commitment to grow our international presence and resources, while markedly increasing the investment in R&D and integration services. You can expect to see an acceleration in the development and availability of new technologies, with deeper absorption of specific business use cases.”
The current plan with our investors is for Robert Stalick, CEO of Tresys, to lead the merged company. Michael Timan, CEO of Owl Cyber Defense, will continue to actively work alongside Bob in developing the vision, applying diligent process focus, and maintaining the sales and services engagement excellence for which we strive. “Our shared goal is nothing less than defining the future of network boundary security technology for the coming decades.”
VMware To Acquire all outstanding shares of Pivotal
I saw this story on Launch Ticker newsletter from CNBC.
Pivotal Software surges after VMware says it’s in talks to acquire the company.
Highlights:
- VMware contributed to the formation of Pivotal in 2013.
- Pivotal stock has fallen 66% in the past year.
Pivotal shares rose as much as 72% premarket Thursday August 15 after VMware said Wednesday it’s proceeding with an agreement to acquire all outstanding shares of Pivotal’s class A stock at $15 per share in cash, an 80.7% premium on Pivotal’s $8.30 closing price.
VMware also said in a regulatory filing that it has requested that Dell exchange all outstanding shares of Pivotal’s class B stock, other than class B Pivotal shares owned by VMware, for Class A VMware stock. Dell controlled almost 81% of VMware’s outstanding common stock and more than 97% of the combined voting power of VMware’s outstanding stock as of May 3. Dell and Pivotal are negotiating an exchange ratio for the shares.
The transaction could contribute to the further diversification of VMware, which has moved to collaborate with cloud infrastructure providers like Amazon in order to enable existing customers to run their computing workloads in whatever environment they like.
Shares of Pivotal have declined 66% in the past year. On June 5 Pivotal stock declined 41% after the company issued guidance that was below what analysts were expecting.
Pivotal went public in April 2018. VMware and DellEMC both contributed assets when Pivotal was established in 2013.
As a result of an agreement with Dell, VMware is the selling agent for certain Pivotal products, such that VMware collects cash that is then remitted to Pivotal, net of a contractual agency fee. As of May 3, VMware had a 16% financial interest in Pivotal and a 24% voting interest in the company.
In a statement of its own, Pivotal said on Wednesday that although it is in talks with VMware about a “potential business combination,” an agreement has not been made.

by Gary Mintchell | Sep 26, 2018 | Internet of Things, Leadership
Browsing LinkedIn, something I seldom do, I saw this image from a company called Seebo. “Where IoT Projects Fail.” Interesting, but can’t these be summed up in a word or two?
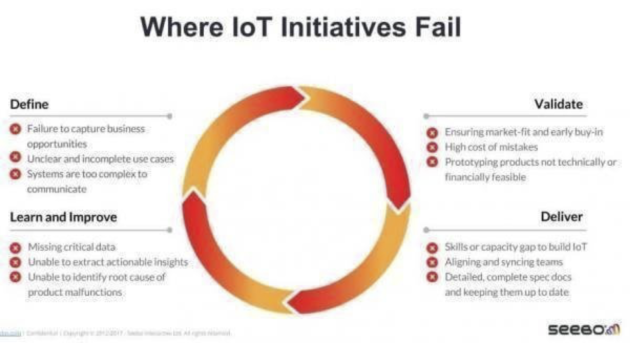
Try “management” or “leadership”.
The recurring theme I’ve found in my consulting and qualification process for a client concerns not really understanding what Internet of Things (IoT) means. Nor do they always understand realistically what benefits could accrue. Or what technologies fit.
A client one time hired me to justify a decision already made—in their minds at least—about acquisitions that would enter them into the IoT market. Another looked for use cases and settled on one not understanding the complexity of that use case.
On the other hand, a wise CTO once explained to me about themes for the company’s annual conference. One year might be IoT and another digitalization. He said they looked at the current themes in the market and then figured how their products fit, and presto—a theme.
If you are in an IoT project or contemplating one as a user or looking at a product and service plan as a supplier, step back and try using good basic management first. Organizing, defining, staffing.
Here is the list from the image:
- Failure to capture business opportunities
- Unclear and incomplete use cases
- Systems are too complex to communicate
- Missing critical data
- Unable to extract actionable insights
- Unable to identify root cause of product malfunctions
- Ensuring market-fit and early buy-in
- High cost of mistakes
- Prototyping products not technically or financially feasible
- Skills or capacity gap
- Aligning and syncing teams
- Detailed and complete spec docs and keeping them up-to-date
by Gary Mintchell | Jan 20, 2016 | Automation, Internet of Things, Networking, Operations Management
 Everyone is in a rush to get an opinion or observation published about the Internet of Things. Evidently it gets lots of page views. Recently other analysts have been publishing thought pieces on IoT in Industry. It appears they have reached the same conclusion that I first broached a couple of years ago. The IoT is not a “thing.” To make any sense of it and use it for any strategy, it must be thought of as an ecosystem encompassing a variety of technologies.
Everyone is in a rush to get an opinion or observation published about the Internet of Things. Evidently it gets lots of page views. Recently other analysts have been publishing thought pieces on IoT in Industry. It appears they have reached the same conclusion that I first broached a couple of years ago. The IoT is not a “thing.” To make any sense of it and use it for any strategy, it must be thought of as an ecosystem encompassing a variety of technologies.
Here is an article that appeared in the Sloan MIT Management Review. Since I am a subscriber, I don’t know if you can see the article at this link.
The writer is Sam Ransbotham is an associate professor of information systems at the Carroll School of Management at Boston College and the MIT Sloan Management Review Guest Editor for the Data and Analytics Big Idea Initiative. He suggests, “The Internet of Things will bring huge changes to the way markets and businesses work — and it could get messy.”
Here is a bromide that I’ve read a thousand times, “Most businesses aren’t ready for the changes to the marketplace that the Internet of Things will bring. But the time to prepare for them is now.”
Actually most business adapt. Some are visionary and will develop new products, processes, and services–and make a lot of money. Others will adapt and survive. Still others will wonder what happened and die. That is the way of business for at least 5,000 years.
Use Case for Internet of Things
“Yes, the potential insights from IoT are enticing. For example, it’s fun to think about the potential personal and even societal benefits from self-driving cars, such as fewer accidents, no problems with parking, more productivity while traveling, car sharing, greater infrastructure efficiency, etc. But perhaps a more profound implication is the data that they can collect. These cars will also be widely distributed “things,” gathering performance data that can help manufacturers diagnose problems, operational data that can help mechanics prevent failures, driver data that can help insurers understand risk, road data that can help cities improve infrastructure, etc. These kinds of insights, we’re ready for.”
But there are a lot more changes coming with the IoT transformation than many people may recognize.
Ransbothem looks into information technology as a model for what will happen in IoT. “About a decade ago, advances in information technology converged to fuel a boom in corporate use of analytics. First, widespread implementation of information systems captured unprecedented amount of data in ways that could be used in isolation or combined. Second, tools and technologies allowed the inexpensive storage and processing. Third, savvy analytical innovators creatively combined these to show everyone else what could be done.”
We have seen all this play out in industrial systems. There remains more to be done, here, though.
He proceeds to look at Internet of Things. “First, the cost and physical size of sensor technology have dropped such that they can be incorporated into most items. Second, widespread communications infrastructure is in place to allow these distributed components to coordinate. Third, once again, savvy innovators are showing the rest of us the possibilities from the data they collect.”
Manufacturing and production are not only poised to exploit these technologies and strategies, they have already been implementing to one degree or another. But his point is valid. IoT needs the ecosystem of sensing devices, networking, communication technology, databases, analytics, and visualization.
Ransbothem identifies four areas of change. Of these, I direct your attention to the last–process changes. I think everything feeds into process changes–not just the processes to make things, but also the information technology, supply chain, and human processes that must not only adapt but thrive with the new information awareness.
- Market Power: IoT should provide a greater amount and a greater value of data, but are companies ready to align their interests in obtaining value from this data with the multiple other companies and end users who create, own, and service the products that originate the data? In the driverless car example, it is easy to see how multiple stakeholders could make use of the data from cars; the same is true for other devices. But it may not be clear who owns what data and how it can be used.
- Complexity: Few organizations are prepared to be hardware and software development companies. But that’s what the Internet of Things will enable. As products are built with embedded sensors, the component mix increases in complexity. As a result, manufacturing systems and supply chains will become more elaborate. Software embedded in products will need to be updateable when the inevitable shortcomings are found.
- Security: If we believe data is valuable, then we need to be ready for people to want to take it from us — why would data be any different than any other precious item? The IoT context intensifies the need for security requirements; for example, sensors or software that allow physical control of the product make attacks easier.
- Process Changes: Many business processes continue to be “pull” oriented. Information is gathered, then analyzed, then decisions are made. This works when change is slow. But with the IoT transition, data will stream in constantly, defying routine reporting and normal working hours. Flooding data from IoT devices will give opportunities for quick reaction, but only if organizations can develop the capacity needed to take advantage of it. Few mainstream large companies are ready for this, much less small- to medium-sized companies that lack the resources of their larger corporate brethren.
The Internet of Things is bringing and will continue to bring advances in how we do business. How well will executives, managers, and engineers execute on this vision? That is key.

by Gary Mintchell | Oct 15, 2015 | Automation, News, Operations Management, Technology, Wireless
 This is a long post, but it brings together several of the more important announcements from this week’s conference. I’ve seen bits of this coming as Emerson has moved its message to incorporate asset management over the past couple of years and is now taking the message to an even higher level in the customer organization. I find it interesting that it takes a holistic look at its product portfolio and then bundles it in such a way as to serve a higher purpose at the customer’s business.
This is a long post, but it brings together several of the more important announcements from this week’s conference. I’ve seen bits of this coming as Emerson has moved its message to incorporate asset management over the past couple of years and is now taking the message to an even higher level in the customer organization. I find it interesting that it takes a holistic look at its product portfolio and then bundles it in such a way as to serve a higher purpose at the customer’s business.
Steve Sonnenberg, Emerson EVP and Emerson Process Management president, said during the opening keynote to Emerson Global Users Exchange 2015, “Managers are looking for dramatic improvements. This is not a time to be satisfied to be as good as everyone else. All are talking top quartile performance. What do you do when all the usual approaches no longer work? Top companies are finding all new approaches. “
The phrase of the day was “Top Quartile Companies.”
Then the concept of improvements in project management and execution was introduced. Jim Nyquist, president of Emerson Systems and Solutions business, added, “Projects are in crisis. 65% of industry’s projects over $1 billion are failing. 33% of projects of $500 million. It seems the larger the project the larger the overrun.”
Global market means more competition leading to increases in the scale of projects.
What’s needed to rein in this runaway stage coach? Nyquist declared that design, engineering, and project management need a reset. Budgets need a resent and predictability and reliability must be improved. Top quartile projects are completed at half the cost and half the schedule of 4th quartile companies. “Industry is at inflection point,” he predicted.
Project Certainty
Then he announced the launch of Project Certainty, an innovative technology- and engineering-based approach for improved capital efficiency and more reliable project schedules.
Emerson’s Project Certainty begins with early engagement during engineering and design studies to define project goals and high impact strategies to meet those goals. Despite traditionally accounting for approximately 4 percent of a project investment, automation is revealing unique and repeatable ways to eliminate cost, reduce complexity and accommodate late-stage project changes, beyond the automation discipline.
For example, Project Certainty relies on the right design engineering strategy to eliminate centralized control system room requirements by 70 to 80 percent, and can eliminate piping in some applications up to 50 to 60 percent. Additionally, tens of millions of dollars in capital spare parts can be eliminated through project-wide equipment reliability analysis.
“Project Certainty also tackles complexity by decoupling the dependencies suppliers have on each other, eliminating bottlenecks and allowing concurrent work streams,” said Nyquist. “Likewise, we are addressing the complexity of data and documentation with innovative technologies that provide features like a single source of project data as well as automated documentation.”
Addressing one of the greatest project vulnerabilities, Project Certainty significantly improves project schedule performance. Technologies like Electronic Marshalling with CHARMs, and pervasive wireless field instrumentation are helping project teams accommodate inevitable last-minute design changes without impacting schedule.
“The path to Top Quartile project performance is right in front of us,” said Nyquist. “The technologies and proven methodologies are here. It will take collaboration and commitment to eliminate outdated project approaches and drive change into the industry.”
Data Link
Part of this new environment is Project Data Link, a project engineering environment that helps reduce complexity and accommodate changes in capital projects. As projects become more complex with multiple contractors and stakeholders, Project Data Link helps keep projects off the critical path by efficiently and consistently translating project information, including tag databases and instrument indices, from multiple sources into project deliverables. It mitigates project risk by normalizing specifications into a single data source with traceability and an integrated change-management system.
Project Data Link gives multiple suppliers, engineering firms, and other stakeholders access to project information including specifications related to field devices and the distributed control system (including control logic and configuration). In addition, data provided in various formats are normalized so that all information is available in a single, consolidated standard view.
The integrity of project information is especially important during late project changes. The data link is always up to date, so when a change is initiated Project Data Link automatically reconciles it against what is in the system, identifies what needs to be changed, automatically sends updates to the DeltaV distributed control system and provides an audit trail of what has changed. This saves time and eliminates errors during the critical late stages of the project.
“Moving forward to improve project certainty, Emerson continues to find methods to reduce the risk of project errors, accommodate change and improve engineering efficiency,” said Randall Fong, project technical manager. “We are confident that Project Data Link will help our customers move towards on-budget and on-time projects.”
Smart Commissioning
Here is yet another part of the portfolio of improving products–Smart Commissioning, a technology-enabled process that reduces automation commissioning time and effort. Smart Commissioning helps automation projects meet strict and shifting deadlines by reducing trips to the field, eliminating tasks, and accommodating late project changes. Smart Automation Commissioning builds on advances made possible by the combination of the DeltaV distributed control system (DCS) Electronic Marshalling with CHARMs and AMS Device Manager Software to remove automation from the critical path of projects.
With the release of version 13 software for the DeltaV DCS and AMS Suite, Smart Commissioning brings ease to automation project implementation. From the initial device connections to final system testing, users save money as they shave weeks off the project schedule by reducing time spent on automation commissioning activities.
Upon arrival at a project site, pre-tagged smart devices can be connected immediately to any channel in a nearby junction box — no need to wait for wiring designs to be complete. Smart Commissioning also eliminates potential errors by automatically finding and identifying all smart devices, then binding them to the configuration. To further accelerate implementation, the device configuration is pushed to all devices based on pre-configured templates. Testing is easily and safely done from the control room by using digital communication, requiring no personnel in the field for confirmation.
“With Smart Commissioning, members of the project team can more easily meet tight project timelines and are not hampered by late design changes,” said Mark Howard, vice president of project execution for Emerson Process Management. “Developed based on industry experience, this solution is another step from Emerson toward attaining project certainty for users.”
Projects in Action
Sasol, an international energy and chemical company, has selected Emerson Process Management to help automate its $8.9 billion petrochemical complex in Lake Charles, La., designed to take advantage of abundant, low cost natural gas. The automation project is one of the largest in history awarded to Emerson.
When completed sometime in 2018, the massive petrochemical complex will more than triple Sasol’s chemical production capacity in the United States. The complex includes an ethane cracker that will produce 1.5 million tons of ethylene annually, as well as six chemical manufacturing plants designed to convert the ethylene into a diverse range of chemicals. Ethylene is a key ingredient in the production of plastics, detergents, anti-freeze, and other petrochemical products.
Emerson Process Management implemented a detailed engineering and project execution plan designed to mitigate project risks, lower costs and reduce time to completion, all part of the company’s strategic Project Certainty initiative.
“For a project of this scale, managing budget and schedule risk is paramount,” said Jim Nyquist, group vice president of Emerson. “This is a great example of our Project Certainty initiative. Early engineering and design work is being used to identify opportunities for automation technology to reduce complexity, create project cost savings, and reduce schedule and cost risks. As the project moves into the execution phase, Emerson is well-positioned to implement the design, accommodate late changes and reduce on-site work – all of which speed execution without compromising quality, safety or reliability.”




 Everyone is in a rush to get an opinion or observation published about the Internet of Things. Evidently it gets lots of page views. Recently other analysts have been publishing thought pieces on IoT in Industry. It appears they have reached the same conclusion that I first broached a couple of years ago. The IoT is not a “thing.” To make any sense of it and use it for any strategy, it must be thought of as an ecosystem encompassing a variety of technologies.
Everyone is in a rush to get an opinion or observation published about the Internet of Things. Evidently it gets lots of page views. Recently other analysts have been publishing thought pieces on IoT in Industry. It appears they have reached the same conclusion that I first broached a couple of years ago. The IoT is not a “thing.” To make any sense of it and use it for any strategy, it must be thought of as an ecosystem encompassing a variety of technologies.





