
by Gary Mintchell | Jun 18, 2018 | Internet of Things, Manufacturing IT
The Industrial Internet Consortium (IIC) generates much useful information promoting awareness and technical tips about, well, the Industrial Internet of Things. Last week I had the opportunity to speak to the authors of a new white paper, ”Introduction to Edge Computing in IIoT”, Todd Edmunds, Senior Solution Architect, IoT, Cisco, and Lalit Canaran, VP, SAP.
The paper provides practical guidance on edge computing, architectures and the building blocks necessary for edge computing implementations. The IIC is also planning to release an Edge Computing Technical Report that will contain in-depth technical information in the coming months.
This paper is not a C-level generic paper evangelizing the concept, but rather practical advice designed to open the discussion followed by technical details targeted to those to whom the C-level executives might tell, “I have been reading about the IIoT. This looks like something we should be jumping into.”
We discussed how the edge should be defined by the business objective rather than the technology used. Using computing at the edge improves performance of the system when bandwidth could be the constraining factor for using the cloud.
As the edge gets more powerful, they told me, the role of the cloud will shift to one of orchestration of remote sites plus storage.
“Many companies are wanting to realize the business benefits that edge computing is purported to provide but are unsure where to begin or how to realize those advantages. The IIC has been at the vanguard of the industrial internet since its inception, and edge computing has been an integral part of driving the transformational outcomes that go along with it,” said Edmunds. “With the publication of this white paper, we provide practical guidance on where the ‘edge’ is and the key drivers for implementing edge computing. We also provide detail on edge computing architectures and real-world use cases.”
“Almost every use case and every connected device on the industrial internet requires some sort of compute capability at its source at the edge,” said Dr. Mitch Tseng, Distinguished Consultant, Huawei Technologies, and co-author of the white paper. “Oil rigs in remote locations have sensors gathering data but they need to be mindful of the challenges of data transmission because of bandwidth issues or the cost of transmission. The white paper is a first step in the development of an industrial grade ‘cookbook’ for edge computing.”
“Organizations adopting an IIoT strategy need to understand what data is available, how to use it to drive industrial processes and how to orchestrate, manage and secure data/compute,” said Canaran. “This paper and subsequent technical report will enable enterprises to unlock the full potential of the edge-cloud continuum and drive the business outcomes enabled by next-generation IoT devices, machine learning and AI.”
The full IIC Introduction to Edge Computing in IIoT white paper and a list of IIC members who contributed can be found on the IIC website.

by Gary Mintchell | May 14, 2018 | Automation, Networking, News, Standards
Hannover Messe continues to reflect the trend of companies joining alliances to develop and promote standards and interoperability. While I did not have an interview with the Avnu Alliance while I was in Hannover, I talked with some members and obtained other information. Avnu Alliance promotes adoption of the Time Sensitive Networking (TSN) extension to Ethernet.
Specifically, Avnu Alliance is a community creating an interoperable ecosystem of low-latency, time-synchronized, highly reliable networked devices using open standards. Avnu creates comprehensive certification programs to ensure interoperability of networked devices. The foundational technology enables deterministic synchronized networking based on IEEE Audio Video Bridging (AVB) / Time Sensitive Networking (TSN) base standards. The Alliance, in conjunction with other complimentary standards bodies and alliances, provides a united network foundation for use in professional AV, automotive, industrial control and consumer segments.
The adoption pace of TSN from 2017 to 2018 was amazing.
I always drop by the Industrial Internet Consortium (IIC) area at Hannover and check out the TSN Testbed for Flexible Manufacturing. The testbed was developed with two major goals – to show TSN’s readiness to accelerate the marketplace; and to show the business value of TSN in converged, deterministic IIoT networks. Momentum is increasing for the testbed, with the IIC hosting its 10th plugfest in an 18-month timeframe at the Bosch Rexroth facility in Frankfurt, Germany and its 9th plugfest, which was held in Austin, TX in February at National Instruments (NI) headquarters following a joint workshop on interoperability with Avnu Alliance. The TSN Testbed recently integrated test tools from Avnu Alliance members, Calnex, Ixia and Spirent into plugfest activities, and demonstrated interoperability of TSN devices from more than 25 companies performing real-time automation and control automation functions over TSN.
Any Avnu Alliance member is welcome to join the IIC TSN Testbed or to participate in a plugfest. Upcoming plugfests will be held in Austin, TX from June 26-29, 2018 and in Stuttgart from July 24-27, 2018.
The Edge Computing Consortium (ECC) along with members and Avnu Alliance, hosted a press conference to announce new developments surrounding the newly created OPC UA TSN testbed. The testbed demonstrates six major IIoT scenarios mimicking processes found in smart manufacturing settings and utilizing products across different TSN vendors. Avnu Alliance is a key partner supporting the development of the testbed with the ECC in the shared goal of enabling manufacturers to test their products for interoperability and conduct trials of real-world systems as an early check for problems.
Tom Weingartner, Avnu Alliance member and Analog Devices’ marketing director for Deterministic Ethernet Technology Group, represented the Alliance at an announcement ceremony.
Paul Didier, Avnu Alliance member and IoT solutions architect, Cisco delivered a talk at the Industrie 4.0 meet the Industrial Internet Forum, in a presentation titled “Time Sensitive Networks – Where does the technology stand and what to expect”. He will provide an update on TSN and how manufacturers, alliances and liaison groups are working together to advance the technology and its implementation in the IIoT.
Paul will present an additional lecture for the Forum on “Modernizing Your Industrial Manufacturing Network”. The presentation will follow the findings coming out of the IIC TSN Testbed and its capabilities, including information on how manufacturing automation and control infrastructure vendors and key decision-makers can leverage TSN for a variety of operational benefits, including increased connectivity between devices and the ability to extract and analyze valuable information through interconnectivity.
“HANNOVER continues to be a key industry event for both Avnu Alliance members and liaison groups that we work with to educate and increase awareness of TSN as a solution for the growing IIoT,” said Todd Walter, Avnu Alliance Industrial Segment Leader and Chief Marketing Manager at NI. “Whether through the developments coming from the TSN testbeds, speaking engagements or product demonstrations, our members and partners are committed to creating an interoperable TSN network that gives all industrial devices a more streamlined path to participating in the TSN ecosystem.

by Gary Mintchell | Apr 24, 2018 | Automation, Manufacturing IT, Technology
Most of my time involves Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) where I am devoting about 2.5 hours a day to interviews. As one person asked, what does HPE have to offer. Briefly described, HPE has a variety of compute devices, services, and partnerships.

One application was a prescriptive maintenance solution where IoT data is analyzed and the CMMS is notified to initiate a work order. We are not in the era of self-healing machines, yet, but we are one step closer where the machine can begin a maintenance workflow with information about what to repair.
The SecureEdge Data Center combines enclosures from Rittal, I/O from ABB, and Edgeline edge computing hardware from HPE into a scalable industrial center to provide IIoT data to the enterprise from ABB robotics and automation.
As a former machine vision integrator, I loved the video analytics demo application showing Relimetrics software to analyze servers in manufacturing. In this case, the application read a 2D barcode to determine the build, discovered the bill of materials, and then checked that all the proper components were in the assembly, that everything was properly installed, and there were no other defects.
One application of Edgeline edge compute devices, for example, is in partnership with National Instruments to accomplish complex testing at the edge with communication to the cloud as necessary. Edge compute is also important in autonomous vehicles where decisions must be quickly executed locally, but large amounts of data must also be communicated to the cloud for further analysis.
Speaking of partnerships, HPE has forged significant partnerships in the industrial world with ABB, GE Digital, OSIsoft, PTC (Kepware and ThingWorx), Rittal, and Schneider Electric. Most of these involve a significant IT infrastructure including power at the Edge from HPE along with data and connectivity plus solutions targeted to various industrial applications.

by Gary Mintchell | Apr 12, 2018 | Internet of Things, Manufacturing IT, Software
The Internet of Things ecosystem is changing computing in almost a seismic shift. But like geology, it builds up over time and then the event happens before you know it.
We had centralized, on-site computing revolutionized by PCs. We networked PCs and wound up with centralized computing in the cloud. Demands from building the Internet of Things (or Industrial Internet of Things for us manufacturing and production geeks) expose the flaws of cloud computing. The next hot thing—edge.
Yesterday the CEO/co-founder of Zededa talked with me about the computing platform his company is building with no less a mission than to build the largest computing company on Earth without owning infrastructure. Its vision—create a new edge economy that allows applications to run anywhere.
Some of what follows may sound familiar. I’ve talked with many companies doing a piece of what Zededa has laid out, but none are as audacious as this.
In brief, Zedeta…
- Closes $3.06M in Seed Funding
- Pioneering a secure, cloud-native approach to real-time edge applications at hyperscale for solutions ranging from self-driving cars to industrial robots
- Built a team comprised of distinguished engineers from top tech companies in cloud, networking and open source to solve the edge computing puzzle and disrupt the status quo
- Seed round was led by Wild West Capital; other investors include Almaz Capital, Barton Capital and Industry Veteran Ed Zander, former CEO of Motorola and former COO of Sun Microsystems
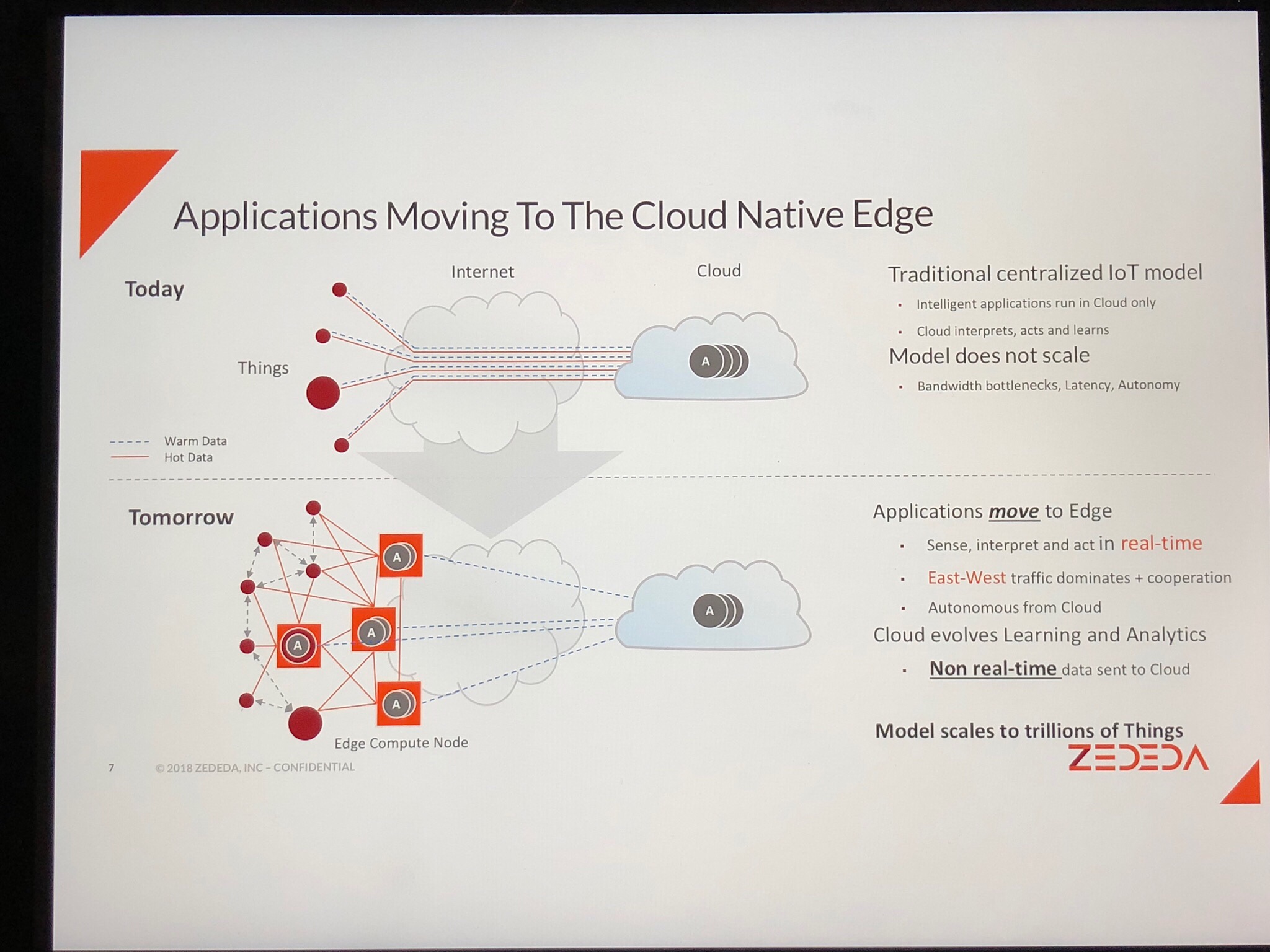
“Tomorrow’s edge computing environment that enables digital transformation will be distributed, autonomous and cooperative. The edge is complex and not only has to scale out securely, but simultaneously must become friendlier for app developers. That’s the problem we are solving at ZEDEDA,” stated ZEDEDA CEO and Co-Founder Said Ouissal. “It will require a drastic shift from today’s embedded computing mindset to a more secure-by-design, cloud-native approach that unlocks the power of millions of cloud app developers and allows them to digitize the physical world as billions of ‘things’ become smart and connected.”
ZEDEDA will use the funding for continued research and product development, investment in community open-source projects for edge computing as well as further investment in sales and marketing initiatives. ZEDEDA investors include Wild West Capital and Almaz Capital, whose funding was part of a broader group investors, some of whom also invested in IoT/edge companies Theatro and Sensity Systems (now Verizon).
In the coming wave of pervasive computing, real-time apps, cyber-physical systems and data services such as machine learning and analytics will become commonplace. ZEDEDA envisions an open ecosystem and a completely new technology stack that creates a service fabric essential to achieving the hyperscale that will be required in edge computing.
To realize that goal, ZEDEDA has pulled together a distinguished roster of industry veterans from legendary technology companies with expertise in areas of operating systems, virtualization, networking, security, blockchain, cloud and application platforms. This unique blend of skills combines with the team’s deep connections to core open-source projects and standardization bodies. The team’s work has directly contributed to software and system patents as well as industry standards used by billions of people around the world today.
“A new paradigm and massive innovation is needed to meet demand for IoT and edge computing,” said Kevin DeNuccio, Founder of Wild West Capital and ZEDEDA’s lead investor. “Massive shifts in technology, including the proliferation of IoT, paves the way for industry disruption, which large incumbents tend to inhibit. Disruption takes a combination of an entrepreneurial team with a very unique set of collective experience, groundbreaking ideas, and the ability to garner immediate traction with global industrial leaders, who can transform their business with machine learning and artificial intelligence delivered by the Edge connected IoT world. ZEDEDA is simply one of the most promising edge computing startups out there.”
“Operations Technology teams face major challenges when it comes to fully realizing the advantages of an IoT world. Their worlds are becoming massively connected systems dealing with virtualization, networking and security,” stated Christian Renaud, Research Director, IoT at 451 Research. “Our recent research shows that while OT teams have the application plans for leveraging IoT, the vast majority of organizations’ IT resources and capabilities are maxed out. This leaves open the question of how these edge applications and IoT will scale out without compromising security or taxing resources even further in the future.”
Ouissal told me, “Edge is the next big wave, bigger than cloud, simply because of the sheer size of the number of devices. The goal is ubiquitous compute where applications want to interact real-time. The problem with the cloud is that it’s centralized. This ecosystem is truly Cyberphysical—just like your Industry 4.0.”
The current IoT model of sending all data to the cloud for processing, won’t scale due to:
- Bandwidth
- Latency
- Privacy issues
Three problems that the company is attacking:
1. Moving apps now running in the cloud to the edge
2. Edge-to-edge communication, key for autonomous systems, peer-to-peer
3. Security, cloud requires cyber security, but at the edge we must add physical security—someone could walk in and carry out an intelligent device
Ouissal often mentioned the need to rethink management of the edge. There exists a big difference between managing cloud and edge. Zedeta is tacking the variety of management challenges for updating and managing thousands to millions of embedded devices.
Solutions the team are developing include:
1. Security-built on platform, use keys, trusted, health check with every plug in, embedded virtualization
2. management-virtualization->can run multiple sessions on a device, eg robot motion on one session and analytics on another all on same embedded system, can scale this to millions of devices
3. Networking-monitor, watch lists, anomaly detection, analyze why, VPN architecture
This is all fascinating. I can’t wait to talk with competitors and potential competitors in a couple of weeks in Hannover and during some upcoming trips to get responses.

by Gary Mintchell | Mar 20, 2018 | Automation, Data Management, Internet of Things, Operations Management
Much of the interesting activity in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) space lately happens at the edge of the network. IT companies such as Dell Technologies and Hewlett Packard Enterprise have built upon their core technologies to develop powerful edge computing devices. Recently Bedrock Automation and Opto 22 on the OT side have also built interesting edge devices.
I’ve long maintained that all this technology—from intelligent sensing to cloud databases—means little without ways to make sense of the data. One company I rarely hear from is FogHorn Systems. This developer of edge intelligence software has recently been quite active on the partnership front. One announcement regards Wind River and the other Google.
FogHorn and Wind River (an Intel company) have teamed to integrate FogHorn’s Lightning edge analytics and machine learning platform with Wind River’s software, including Wind River Helix Device Cloud, Wind River Titanium Control, and Wind River Linux. This offering is said to accelerate harnessing the power of IIoT data. Specifically, FogHorn enables organizations to place data analytics and machine learning as close to the data source as possible; Wind River provides the technology to support manageability of edge devices across their lifecycle, virtualization for workload consolidation, and software portability via containerization.
“Wind River’s collaboration with FogHorn will solve two big challenges in Industrial IoT today, getting analytics and machine learning close to the devices generating the data, and managing thousands to hundreds of thousands of endpoints across their product lifecycle,” said Michael Krutz, Chief Product Officer at Wind River. “We’re very excited about this integrated solution, and the significant value it will deliver to our joint customers globally.”
FogHorn’s Lightning product portfolio embeds edge intelligence directly into small-footprint IoT devices. By enabling data processing at or near the source of sensor data, FogHorn eliminates the need to send terabytes of data to the cloud for processing.
“Large organizations with complex, multi-site IoT deployments are faced with the challenge of not only pushing advanced analytics and machine learning close to the source of the data, but also the provisioning and maintenance of a high volume and variety of edge devices,” said Kevin Duffy, VP of Business Development at FogHorn. “FogHorn and Wind River together deliver the industry’s most comprehensive solution to addressing both sides of this complex IoT device equation.”
Meanwhile, FogHorn Systems also announced a collaboration with Google Cloud IoT Core to simplify the deployment and maximize the business impact of Industrial IoT (IIoT) applications.
The companies have teamed up to integrate Lightning edge analytics and machine learning platform with Cloud IoT Core.
“Cloud IoT Core simply and securely brings the power of Google Cloud’s world-class data infrastructure capabilities to the IIoT market,” said Antony Passemard, Head of IoT Product Management at Google Cloud. “By combining industry-leading edge intelligence from FogHorn, we’ve created a fully-integrated edge and cloud solution that maximizes the insights gained from every IoT device. We think it’s a very powerful combination at exactly the right time.”
Device data captured by Cloud IoT Core gets published to Cloud Pub/Sub for downstream analytics. Businesses can conduct ad hoc analysis using Google BigQuery, run advanced analytics, and apply machine learning with Cloud Machine Learning Engine, or visualize IoT data results with rich reports and dashboards in Google Data Studio.
“Our integration with Google Cloud harmonizes the workload and creates new efficiencies from the edge to the cloud across a range of dimensions,” said David King, CEO at FogHorn. “This approach simplifies the rollout of innovative, outcome-based IIoT initiatives to improve organizations’ competitive edge globally, and we are thrilled to bring this collaboration to market with Google Cloud.”








