
by Gary Mintchell | Aug 24, 2018 | Automation, Operator Interface, Technology, Workforce
Simulators are great training tools. It sure beats flying 777s around for your annual pilot recert. Gaming technology has become so good along with many other technologies, that operators of process plants and machinery should be well trained to respond appropriately to any emergency.
Georgia Institute of Technology sent this information about an advancement in simulation for operator training. Good stuff.
A simulator that comes complete with a virtual explosion could help the operators of chemical processing plants – and other industrial facilities – learn to detect attacks by hackers bent on causing mayhem. The simulator will also help students and researchers understand better the security issues of industrial control systems.
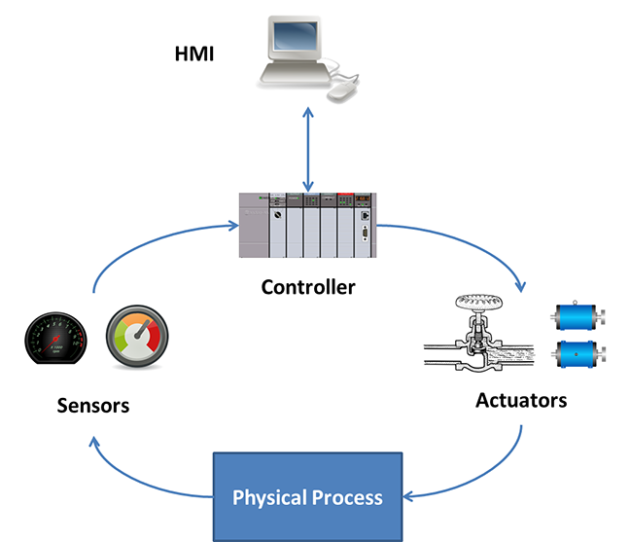
This flow chart shows data flows within a simulated chemical processing facility.
Facilities such as electric power networks, manufacturing operations and water purification plants are among the potential targets for malicious actors because they use programmable logic controllers (PLCs) to open and close valves, redirect electricity flows and manage large pieces of machinery. Efforts are underway to secure these facilities, and helping operators become more skilled at detecting potential attacks is a key part of improving security.
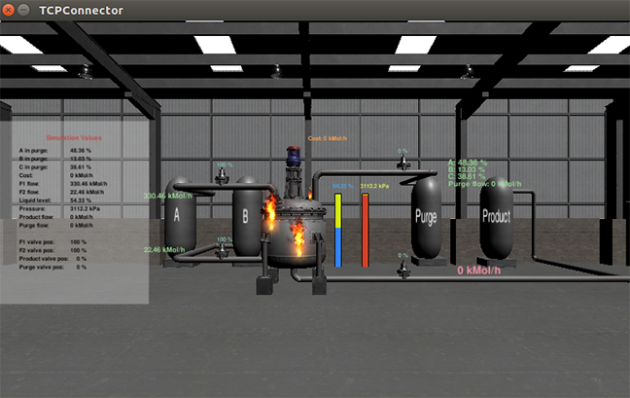
Screen captures show a simulated explosion in a chemical processing plant precipitated by a cyberattack on the system.
“The goal is to give operators, researchers and students experience with attacking systems, detecting attacks and also seeing the consequences of manipulating the physical processes in these systems,” said Raheem Beyah, the Motorola Foundation Professor in the School of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the Georgia Institute of Technology. “This system allows operators to learn what kinds of things will happen. Our goal is to make sure the good guys get this experience so they can respond appropriately.”
Details of the simulator were presented August 8 at Black Hat USA 2018, and August 13 at the 2018 USENIX Workshop on Advances in Security Education. The simulator was developed in part by Atlanta security startup company Fortiphyd Logic, and supported by the Georgia Research Alliance.
The simulated chemical processing plant, known as the Graphical Realism Framework for Industrial Control Simulations (GRFICS), allows users to play the roles of both attackers and defenders – with separate views provided. The attackers might take control of valves in the plant to build up pressure in a reaction vessel to cause an explosion. The defenders have to watch for signs of attack and make sure security systems remain operational.
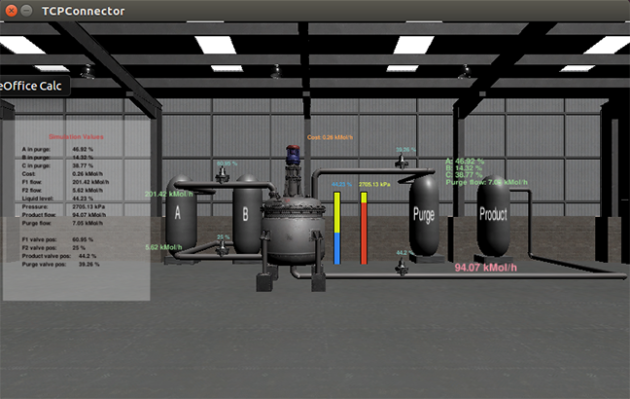
Screen capture shows a chemical processing plant in which critical parameters are rising due to false process data and control commands injected by an attacker.
Of great concern is the “man-in-the-middle” attack in which a bad actor breaks into the facility’s control system – and also takes control of the sensors and instruments that provide feedback to the operators. By gaining control of sensors and valve position indicators, the attacker could send false readings that would reassure the operators – while the damage proceeded.
“The pressure and reactant levels could be made to seem normal to the operators, while the pressure is building toward a dangerous point,” Beyah said. Though the readings may appear normal, however, a knowledgeable operator might still detect clues that the system has been attacked. “The more the operators know the process, the harder it will be to fool them,” he said.
The GRFICS system was built using an existing chemical processing plant simulator, as well as a 3D video gaming engine running on Linux virtual machines. At its heart is the software that runs PLCs, which can be changed out to represent different types of controllers appropriate to a range of facilities. The human-machine interface can also be altered as needed to show a realistic operator control panel monitoring reaction parameters and valve controller positions.
“This is a complete virtual network, so you can set up your own entry detection rules and play on the defensive side to see whether or not your defenses are detecting the attacks,” said David Formby, a Georgia Tech postdoctoral researcher who has launched Fortiphyd Logic with Beyah to develop industrial control security products. “We provide access to simulated physical systems that allow students and operators to repeatedly study different parameters and scenarios.”
GRFICS is currently available as an open source, free download for use by classes or individuals. It runs on a laptop, but because of heavy use of graphics, requires considerable processing power and memory. An online version is planned, and future versions will simulate the electric power grid, water and wastewater treatment facilities, manufacturing facilities and other users of PLCs.
Formby hopes GRFICS will expand the number of people who have experience with the security of industrial control systems.
“We want to open this space up to more people,” he said. “It’s very difficult now to find people who have the right experience. We haven’t seen many attacks on these systems yet, but that’s not because they are secure. The barrier for people who want to work in the cyber-physical security space is high right now, and we want to lower that.”
Beyah and Formby have been working for several years to increase awareness of the vulnerabilities inherent in industrial control systems. While the community still has more to do, Beyah is encouraged.
“Several years ago, we talked to a lot of process control engineers as part of the NSF’s I-Corps program,” he said. “It was clear that for many of these folks then, security was not a major concern. But we’ve seen changes, and lots of people are now taking system security seriously.”

by Gary Mintchell | Mar 19, 2018 | Automation
Whenever people hear about automation or manufacturing technology, they always respond with “robots?”. Reading mainstream media where writers discuss manufacturing without a clue, they also seem fixated on robots. And most all of this ranges from partial information to misinformation. I seldom write about robotics because the typical SCARA or six-axis robots are still doing the same things they’ve always done—pick-and-place, welding, painting, material handling. They are better, faster, more connected, and in different industries, but in the end it’s still the same thing.
That is why I’m a fan of Rethink Robotics. These engineers are out there trying new paradigms and applications. Here is a recent release that I think bears watching. This news is especially relevant in the context of the visit I made last week to Oakland University and conversations with some students.

Rethink Robotics unveiled the Sawyer Software Development Kit (SDK), a software upgrade designed for researchers and students to build and test programs on the Sawyer robot. With a wide range of uses for university research teams and corporate R&D laboratories around the world, Sawyer SDK offers further compatibility with ROS and state-of-art Open Source robotics tools, as well as an affordable solution to increase access to advanced robotics in the classroom.
Sawyer SDK includes several advanced features that allow users to visualize and control how the robot interacts with its environment. Sawyer SDK now integrates with the popular Gazebo Simulator, which creates a simulated world that will visualize the robot and its contact with the environment, allowing researchers to run and test code in the simulation before running it on the robot. Sawyer’s Gazebo integration is completely open source, allowing students to run simulations from their individual laptops without a robot until they’re ready to test the code in real time. This approach allows professors to provide students with access to the industry-leading collaborative robots.
In addition to the Gazebo integration, Sawyer SDK includes a new motion interface that allows researchers to program the robot in Cartesian space. This development lowers the barriers for motion planning for programmers without a full robotics background. The new release also allows researchers to leverage new impedance and force control. Sawyer SDK also includes support for ClickSmart, the family of gripper kits that Rethink announced in 2017 to create a fully integrated robotic solution.
“Rethink’s robots are used in the world’s leading research institutions, which provides us with a wealth of feedback on what our research customers really want,” said Scott Eckert, president and CEO, Rethink Robotics. “As we have with all of our SDK releases, we’re continuing to set the standard in research with industry-leading features that allow universities and corporate labs to push the field of robotics forward and publish their research faster.”
Sawyer SDK is being piloted in robotics programs at multiple universities, including Stanford University, University of California at Berkeley, Georgia Institute of Technology and Northwestern University. Stanford’s Vision and Learning Lab works on endowing robots with diverse skills for both industrial and day-to-day personal robotics applications.
“Robotics is a field that combines technological and engineering skills with creativity, and the inventiveness our students have shown so far with the robots has been astounding,” said Dr. Animesh Garg, postdoctoral researcher in the Stanford University department of computer science. Animesh and his team of researchers have put Sawyer to use executing tasks directly from virtual reality (VR) input using automatic decomposition in simpler activities. Sawyer is also used for ongoing work in learning to use simple tools, such as hammers and screwdrivers.
Stanford University’s Experimental Robotics class allows students to think beyond day-to-day industrial tasks. They’ve trained Sawyer to draw, and track moving targets and hovering drones. Rethink’s Sawyer has enabled faster learning curves for researchers and students alike, making it easier than ever with the Sawyer SDK release.
The SDK will be available on all Sawyer robots, allowing access to both the Intera manufacturing software and the SDK software, starting in March 2018.

by Gary Mintchell | Mar 1, 2018 | Automation, Operations Management
Honeywell released three announcements while I am still recapping the ARC Forum. There are one or two more to go. Thèse regarded maintenance management, simulation, and safety under the umbrella of Connected Plant.
The first is a new offering as part of Honeywell Connected Plant that allows customers to more effectively manage the maintenance and operations of their industrial equipment. The new Honeywell Connected Plant Asset Performance Insight connects the customers’ assets and equipment to the cloud, and applies analytical models from Honeywell and its partners, so that customers can avoid unplanned downtime and unnecessary maintenance.
“In today’s competitive business climate, in which asset capacity is often sold out, equipment performance is key to increased profitability,” said Richard Shaw, general manager, Honeywell Connected Plant. “With operational and maintenance-induced equipment failures accounting for most of the unplanned downtime, industrial companies are looking to digital transformation and IIoT to make sense out of huge amounts of data. Honeywell Connected Plant and our new Asset Performance Insight will help our customers operate more strategically and effectively.”
Honeywell designed the Asset Performance Insight solution to be rapidly deployed to customers through pre-configured templates. These templates are based on the company’s deep industry experience and real-world customer challenges enhanced with advanced analytics. The offering can also be configured and tailored to customers’ specific needs, making it extremely flexible.
The second is a cloud-based simulation tool that uses a combination of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) to train plant personnel on critical industrial work activities. With as much as 50 percent of industrial plant personnel due to retire within the next five years, the Honeywell Connected Plant Skills Insight Immersive Competency is designed to bring new industrial workers up to speed quickly by enhancing training and delivering it in new and contemporary ways.
Honeywell’s advanced training solution combines mixed reality with data analytics and Honeywell’s 25 years of experience in worker competency management to create an interactive environment for on-the-job training. It uses Microsoft’s HoloLens, the world’s first and only self-contained holographic computer, and Windows Mixed Reality headsets to simulate various scenarios for Honeywell’s C300 controller – such as primary failure and switchovers, cable and power supply failure – that train and test personnel on their skills.
“Megatrends such as the aging workforce are putting increased pressure on industrial companies and their training programs,” said Youssef Mestari, program director, Honeywell Connected Plant. “There is a need for more creative and effective training delivered through contemporary methods such as Immersive Competency, ultimately empowering industrial workers to directly improve plant performance, uptime, reliability and safety.”
Simulating specific job activities through virtual environments, which are accessed through the cloud, Honeywell’s solution offers a natural way to interact and communicate with peers or a trainer. Similar to a flight simulator, trainees can safely experience the impacts of their decisions. This approach improves skill retention versus traditional training methods by up to 100 percent and reduces the length of technical training by up to 66 percent. Additionally, the employees’ training progress is tracked as part of a formal competency management system.
And wrapping up is a new solution for real-time safety monitoring of workers in plant and remote operations. Honeywell Connected Plant Skills Insight Personal Gas Safety helps to protect lives and enable faster response in case of hazardous leaks or worker injury.
The solution’s wearable gas detectors monitor gas, radiation and dust, and are tightly integrated with Honeywell’s distributed control system, Experion® Process Knowledge System (PKS). In case of harmful exposures, man-down or panic alarms of workers in the field, accurate, automated alarms now alert control room operators in real time. In addition, safety teams can take advantage of powerful tools embedded in Experion PKS to provide detailed trending, reporting and data analysis of the gas detectors to further ensure safe operations.
“Monitoring worker safety and ensuring proper response to emergencies are top priorities for industrial producers,” said Adrian Fielding, marketing director, Integrated Protective Solutions for Honeywell Process Solutions (HPS). “Personal Gas Safety gives plant operators eyes and ears in the field to improve their situational awareness, helping avoid potentially life-threatening conditions while also providing workers with the assurance that help will be on the way quickly if they need it.”

by Gary Mintchell | Feb 22, 2018 | Automation
Today’s news from the ARC Forum concerns AspenTech and Emerson as we focus on process systems and asset optimization.
Only a few years ago it appeared that AspenTech was destined for some sort of demise—sold for parts or something. It has rebounded nicely since and last week announced enhancements to its production optimization solution and this partnership with Emerson. Collaboration being one of the sub-themes of the conference.
Emerson and AspenTech have teamed up to deliver asset optimization software solutions along with global automation technologies and operational consulting services.
AspenTech’s asset optimization supports Emerson’s Project Certainty and Operational Certainty initiatives. “Emerson’s global footprint, automation engineering services and software, extensive large-scale project execution and consulting capabilities complement AspenTech’s technology footprint. Collectively, these capabilities can be deployed as solutions in both conventional and cloud-based architectures.”
“Emerson and AspenTech are both highly focused on digital technologies and services that deliver measurable improvements and value to our customers’ bottom line,” says David N. Farr, chairman and CEO of Emerson. “Together, we are well positioned to help our customers navigate the best path in this era of digital transformation and achieve Top Quartile performance.” Top Quartile is defined as achieving operations and capital performance in the top 25 percent of peer companies.
The alliance will initially focus on three key areas: engineering software, including high-fidelity simulation to help validate project design and train operators before start-up; manufacturing and supply chain software, including advanced process control software designed for highly complex operations; and asset performance management software to improve plant reliability.
“Working with Emerson, we will help more organizations drive higher total shareholder returns with a relentless focus on operational excellence,” says Antonio Pietri, president and CEO of AspenTech. “We look forward to helping make the best companies even better by optimizing the design, operation and maintenance lifecycle with software and insight to run assets faster, safer, longer and greener.”
Emerson Updates
Meanwhile, Emerson hits themes of security, close to the edge (of the network), and OPC UA among many updates to its process automation system. It is expanding its Plantweb digital ecosystem with the launch of DeltaV version 14, a cybersecurity-certified control system designed to deliver new value in capital projects and make plant operations more connected and productive. The latest release provides significant innovations to the entire DeltaV architecture and was built with customers’ digital transformation initiatives in mind.
This major update to the DeltaV automation system includes several enhancements to eliminate costs and reduce complexity in capital projects, plus improve productivity during operations through enhanced access to production and equipment data, improved usability and greater security.
“More than ever, an integrated plant data environment is essential to achieve digital transformation. With DeltaV, we’re reducing the engineering effort required to securely connect plant, operational and information systems,” said Jamie Froedge, president of Process Systems and Solutions, Emerson Automation Solutions. “Our customers will have more capabilities in their distributed control and safety systems to help them successfully execute capital projects and optimize operations.”
Capital Project Flexibility
Continuing to advance the impact of DeltaV Electronic Marshalling with CHARMs on capital project engineering, CHARM I/O Block takes CHARMs—which achieved more than one million deployments at more than 1100 sites in only five years—closer to the field. Small enclosures with up to 12 CHARMs can now be installed closer to field devices, significantly reducing wiring and overall installation costs by as much as 60 percent and providing more engineering flexibility.
Smart Commissioning, launched in 2016, took one of most engineering intensive operations off a project’s critical path. Traditionally, commissioning has been a manual task that requires more than two hours per device for thousands of devices. Smart Commissioning reduced commissioning time to 25 minutes. Emerson is now expanding these capabilities and reducing device commissioning time to as little as 10 minutes, a nearly 93 percent reduction in costly commissioning time that could save several hundred-thousand dollars in engineering costs.
Mobility and User Experience
DeltaV Live Operator Interface is a modern, built-for-purpose operations experience that is easy to understand and modify. The HMI comes pre-engineered with the industry’s best practices for user experience including ISA 101.01 and is based on research with the Center for Operator Performance, a consortium of vendors and academia focused on human factors engineering. The HTML5 interface enables scalable graphics and gives operators the flexibility to adjust their displays to focus on process data that is most important for each situation. The new operator interface helps improve overall situational awareness and decision-making speed. Emerson is helping companies prepare for the shift to mobility with DeltaV Live by building a foundation for graphics to be transferrable across desktops, laptops, and mobile devices—all without additional engineering or custom scripting.
A Secure, Connected Plant
DeltaV will offer its users a new level of confidence and protection from cybersecurity threats by being one of the only systems to have a top-to-bottom cybersecurity certification. DeltaV v14 will be certified ISASecure SSA Level 1 by the International Society of Automation (ISA), signifying that Emerson developers are trained to write secure code and the system as a whole is hardened against cyber threats.
Emerson is making connecting a plant’s OT systems with IT systems seamless by expanding OPC UA access in its DeltaV hardware and software offerings. DeltaV is the pathway for most plant data and now using the IIoT’s most prevalent protocol, OPC UA, DeltaV applications and servers can securely share data to cloud analytics applications, remote monitoring solutions, and third-party technologies.
by Gary Mintchell | Apr 28, 2016 | Automation, News, Operations Management
 Echos of Industrie 4.0 were present around the Hannover Messe 2016, but times have moved on since 2013. The word of the week was digital–in many forms, such as digitalization, digital enterprise, digital factory.
Echos of Industrie 4.0 were present around the Hannover Messe 2016, but times have moved on since 2013. The word of the week was digital–in many forms, such as digitalization, digital enterprise, digital factory.
Chancellor Merkel and President Obama (two friends says the headline) were not digital, however, as they made a grand tour through parts of the trade fair highlighting the latest manufacturing technologies. And when the US President appears, the rest of the world stops. There were a reported 10,000 police in Hannover. The building I was in during the tour was surrounded by police, we could see snipers on the buildings around us, and we were locked in from 9 am until 1 pm. Fortunately, we had food.
Fortunately also for Siemens, they had a “captive” audience for their press conference for an extra couple of hours.
Siemens captured a large chunk of my time in Hannover. (Disclaimer, two divisions of the company paid some of my expenses.) Because I had some good contacts, I was able to get many interviews and looks behind the scenes. But the main reason I spent much time there was that Siemens had much to show.
Digital Manufacturing Vision
The digital manufacturing vision that Anton Huber laid out for me at the ARC Forum in Orlando in 2006 has progressed considerably. With a backbone of Internet of Things technologies and adding in digital everywhere, Siemens revealed the benefits of bringing everything together.
Take a tour through automobile production, for example. Sebastian Israel took me through the process from designing in Siemens CAD solution (NX), to production planning and engineering (TeamCenter, both from Siemens (PLM). The process continues through designing and engineering the line–digitally of course. Because it is digital first, engineers can simulate the line removing constraints and interferences before any steel is cut.
Integrating the automation and controls to the process is the hardest part of the system. Siemens has begun this process. It does acknowledge much work remains in this area. Mechatronics integration is well along. Things do not stop here, though. TeamCenter helps with change management. TiA Portal enables control engineering collaboration. The process feed the execution level (MES) for production scheduling and other functions including feeding the resource manager of CNC tools to help select the proper next tool to use. This integrates into services–data is usable for such analyses as predictive maintenance.
So far as I can tell, no other company comes close to the ability to do all this within its own umbrella. Although remarkable for what I’d call the “old” Siemens, the “new” Siemens actually uses partnerships to fill the gaps in the system. This is not the same company I met 15 years ago.
I congratulate Mr. Huber for the vision and seeing it through to its current state.
Other Siemens News
Rihab Ehms led a personal tour on TIA Portal Engineering Software. This product continues to develop and flesh out gaps. The first glimpse from a few years ago was pretty much that of an Integrated Development Environment for programming control. Slowly, the Siemens team added drives, HMI, and now motion control and motor management. Also included is energy management. It is a multiuser environment enabling broad collaboration among engineers using a “smart library” concept and common data management.
Ulli Klenk, next on my list, discussed Industrial Additive Manufacturing. I mentioned some interviews I’ve had on additive manufacturing research at North Carolina State. A Duke grad, he was a bit disappointed. His passion showed on the ways Siemens is helping customers with additive manufacturing (also known as 3D printing). Leveraging expertise from Siemens PLM and working with partner machine builders, the company has systems working in a number of application.
Not part of this exhibit but thoroughly fascinating as well, Local Motors sent an engineer to participate in the Siemens booth showing how the company is building a complete car (and now a minibus) using additive manufacturing methods.
The paper industry faces challenges as we all reduce the amount of paper we use. It is searching for alternatives to its product lines. Therefore the broadening of the industry term to “fiber.” Siemens is there, of course, to blend its process control, drive systems, simulation, and predictive maintenance capabilities. Dr. Hermann Schwarz explained the technologies and then said these technologies will help the paper industry broaden into the fiber industry.
One last technology that I didn’t tour but heard much about is MindSphere. Partnering with SAP HANA, this is an industrial cloud providing data driven services and eventually an App Store so that customers can wring the most value possible from their own data.
Not a Chance
When this vision was explained in 2006 and 2007, I didn’t think there was any chance Siemens could pull it off. The pieces are coming together well. They still have much work to do, but customers can certainly benefit right now with increased manufacturing flexibility, product quality, and efficiency.







 Echos of Industrie 4.0 were present around the Hannover Messe 2016, but times have moved on since 2013. The word of the week was digital–in many forms, such as digitalization, digital enterprise, digital factory.
Echos of Industrie 4.0 were present around the Hannover Messe 2016, but times have moved on since 2013. The word of the week was digital–in many forms, such as digitalization, digital enterprise, digital factory.



