
by Gary Mintchell | Aug 6, 2019 | Security, Standards
Standards are useful, sometimes even essential. Standard sizes of shipping containers enable optimum ship loading/unloading. Standard railroad gauges and cars enable standard shipping containers to move from ship to train, and eventually even to tractor/trailer rigs to get products to consumers.
Designing and producing to standards can be challenging. Therefore the value of Best Practices.
Taking this to the realm of Industrial Internet of Things where data security, privacy and trustworthiness are essential, the Industrial Internet Consortium (IIC) has published the Data Protection Best Practices White Paper. I very much like these collaborative initiatives that help engineers solve real world problems.
Designed for stakeholders involved in cybersecurity, privacy and IIoT trustworthiness, the paper describes best practices that can be applied to protect various types of IIoT data and systems. The 33-page paper covers multiple adjacent and overlapping data protection domains, for example data security, data integrity, data privacy, and data residency.
I spoke with the lead authors and came away with a sense of the work involved. Following are some highlights.
Failure to apply appropriate data protection measures can lead to serious consequences for IIoT systems such as service disruptions that affect the bottom-line, serious industrial accidents and data leaks that can result in significant losses, heavy regulatory fines, loss of IP and negative impact on brand reputation.
“Protecting IIoT data during the lifecycle of systems is one of the critical foundations of trustworthy systems,” said Bassam Zarkout, Executive Vice President, IGnPower and one of the paper’s authors. “To be trustworthy, a system and its characteristics, namely security, safety, reliability, resiliency and privacy, must operate in conformance with business and legal requirements. Data protection is a key enabler for compliance with these requirements, especially when facing environmental disturbances, human errors, system faults and attacks.”
Categories of Data to be Protected
Data protection touches on all data and information in an organization. In a complex IIoT system, this includes operational data from things like sensors at a field site; system and configuration data like data exchanged with an IoT device; personal data that identifies individuals; and audit data that chronologically records system activities.
Different data protection mechanisms and approaches may be needed for data at rest (data stored at various times during its lifecycle), data in motion (data being shared or transmitted from one location to another), or data in use (data being processed).
Data Security
“Security is the cornerstone of data protection. Securing an IIoT infrastructure requires a rigorous in-depth security strategy that protects data in the cloud, over the internet, and on devices,” said Niheer Patel, Product Manager, Real-Time Innovations (RTI) and one of the paper’s authors. “It also requires a team approach from manufacturing, to development, to deployment and operation of both IoT devices and infrastructure. This white paper covers the best practices for various data security mechanisms, such as authenticated encryption, key management, root of trust, access control, and audit and monitoring.”
Data Integrity
“Data integrity is crucial in maintaining physical equipment protection, preventing safety incidents, and enabling operations data analysis. Data integrity can be violated intentionally by malicious actors or unintentionally due to corruption during communication or storage. Data integrity assurance is enforced via security mechanisms such as cryptographic controls for detection and prevention of integrity violations,” said Apurva Mohan, Industrial IoT Security Lead, Schlumberger and one of the paper’s authors.
Data integrity should be maintained for the entire lifecycle of the data from when it is generated, to its final destruction or archival. Actual data integrity protection mechanisms depend on the lifecycle phase of the data.
Data Privacy
As a prime example of data privacy requirements, the paper focuses on the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which grants data subjects a wide range of rights over their personal data. The paper describes how IIoT solutions can leverage data security best practices in key management, authentication and access control can empower GDPR-centric privacy processes.
The Data Protection Best Practices White Paper complements the IoT Security Maturity Model Practitioner’s Guide and builds on the concepts of the Industrial Internet Reference Architecture and Industrial Internet Security Framework.
The Data Protection Best Practices White Paper and a list of IIC members who contributed to it can be found on the IIC website
by Gary Mintchell | Jul 8, 2019 | Internet of Things, Manufacturing IT, Organizations
I’ve been off for most of the past week celebrating Independence Day and family birthdays. For those of you in the US, I hope you had a restful time off and enjoyed some fireworks displays. And now, back to what’s happening in the industrial world.
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) comprises far more than just the simple connecting of devices back to a database in a server. It’s integral to digitalization. Applying abundance thinking to the system, clearly IIoT plays a key role for successful business transformation.
The Industrial Internet Consortium (IIC) has produced the IIoT Maturity Assessment, a web-based tool included in the IIC Resource Hub that enables users to better understand their enterprise IIoT maturity. The IIoT Maturity Assessment helps organizations become best-practice adopters of IIoT by guiding business managers through a range of questions about the adoption, usage and governance of IIoT within their organizations.
“The IIoT market has grown quickly and many businesses planned strategy while in the midst of execution and need to step back and assess their true IIoT maturity,” said Jim Morrish, Co-Chair of the IIC’s Business Strategy and Solution Lifecycle Working Group and co-author of the IIoT Maturity Assessment tool. “The IIoT Maturity Assessment will help companies get a baseline for their maturity right now and assess it in regular intervals to track their progress.”
This framework of four main dimensions and their corresponding strands will spur your thinking into broader areas beyond predictive maintenance or cost reduction programs.
The framework:
Business Strategy
- Business model innovation and refinement
Business Solution Lifecycle
- Interface to business strategy
- In service monitoring and feedback
Technology
- Reference architecture and standards
- Data location transparency
Security
“There’s a real difference between using IIoT to streamline processes and using it to create new revenue streams or make better business decisions,” said Ian Hughes, Senior Analyst, Internet of Things, 451 Research. “A tool like this can be a real eye opener for an organization wanting to transform their business to remain competitive and increase profits.”
The IIoT Maturity Assessment considers 63 individual capabilities, each with five levels of maturity within the above framework. For example, under strategic context, a maturity level can range from a limited number of key individuals having stepped up to IIoT ownership to full ownership of IIoT within an organization. The IIoT Maturity Assessment provides feedback about the level of maturity and highlights areas that may require development.
The final outputs provided to users also provide links to the IIC Body of Knowledge for reference and to help improve their maturity. This includes collaborative resources developed by industry leaders from the IIC membership, including IIC foundational documents (Industrial Internet Reference Architecture, Industrial Internet Security Framework, Industrial Internet Connectivity Framework, Business Strategy and Innovation Framework, Industrial Internet of Things Analytics Framework, and Vocabulary Technical Report) and other IIC documents and tools.
The IIoT Maturity Assessment is available in three levels of analysis: Quick, Standard (both open to everyone) and Detailed (IIC members only).

by Gary Mintchell | Feb 3, 2017 | Internet of Things, News, Organizations
 Committee co-chair Mark Crawford of the The Industrial Internet Consortium (IIC) told me yesterday that its Industrial Internet Reference Architecture is a living document. The committee revises frequently in order to stay current with rapidly moving technology and use cases.
Committee co-chair Mark Crawford of the The Industrial Internet Consortium (IIC) told me yesterday that its Industrial Internet Reference Architecture is a living document. The committee revises frequently in order to stay current with rapidly moving technology and use cases.
Therefore, it is no surprise that the organization has published version 1.8 of the Industrial Internet Reference Architecture (IIRA). This new version builds on version 1.7, originally published on June 17, 2015. The document is applicable both for systems architects and business leaders who wish to incorporate the Internet of Things into their corporate strategies.
The IIRA is a standards-based architectural template and methodology designed by a broad spectrum of IIC members, including system and software architects, business experts, and security experts, to assist IIoT system architects to design IIoT solution architectures consistently and to deploy interoperable IIoT systems. It is important to note that the IIRA itself is not a standard.
“The IIC is committed to delivering practical deliverables to the IIoT community that represent the latest thinking about IIoT,” said John Tuccillo, Senior Vice President of Global Industry and Government Affairs, Schneider Electric and IIC Steering Committee Chair. “The IIRA, like all IIC deliverables, is a living document. The IIRA and the now the IIRA v1.8 are the first steps toward an open, innovative and thriving technology development ecosystem across industrial sectors of the IoT.”
“We have already seen customers who are using the IIRA to define and deploy their IIoT systems,” said Dr. Tanja Rueckert, Executive Vice President, IoT and Digital Supply Chain at SAP SE and IIC Steering Committee Vice Chair. “The IIRA and the other IIC deliverables provide significant value to IIC members as well as the broader IIoT and IoT communities.”
IIRA v1.8 Benefits
The IIoT core concepts and technologies addressed in the IIRA v1.8 are applicable to the depth and breadth of every small, medium and large enterprise in manufacturing, mining, transportation, energy, agriculture, healthcare, public infrastructure and virtually every other industry. In addition to IIoT system architects, the plain language of IIRA v1.8 and its emphasis on the value proposition and enablement of converging Operational Technology (OT) and Information Technology (IT) enables business decision-makers, plant managers, and IT managers to better understand how to drive IIoT system development from a business perspective.
“It has been widely recognized that IIoT delivers value and transforms business. A main challenge for many enterprises now is how to get started,” said Shi-Wan Lin, CEO & Co-Founder, Thingswise, LLC and Co-Chair of the IIC Architecture Task Group. “The IIRA provides a framework to drive IIoT projects from a business viewpoint. This is valuable for enterprises to build IIoT systems that can deliver the expected business value.”
Technology vendors can use the IIRA concepts and methodologies to build interoperable system components that address the broadest possible market. System implementers can use the IIRA as a starting point to shorten system development by deploying reusable, commercially available, or open-source system building blocks to reduce project risk, associated costs, and time-to-market. Ultimately, the IIRA will help the IIoT community to realize an open, innovative IIoT ecosystem, thereby reducing the cost of design and operations.
“The value of the IIC is that it brings together a set of diverse, talented people with an extraordinary set of knowledge to develop innovative technology to solve corporate-level industrial challenges,” said Todd Edmunds, Global Manufacturing Solutions Architect – Internet of Things at Cisco Systems and Co-Chair of the IIC Edge Computing Task Group. “The IIRA accelerates the development of solutions to digitize business and realize IIoT’s true potential to transform industry.”
Journal of Innovation
Capping a busy week, the IIC has also published the Third Edition of the Journal of Innovation. A publication written by IIC members, the third edition of the Journal of Innovation is dedicated to the “Smart Factory,” and includes articles on designing, retrofitting, and applying IIoT technologies within the manufacturing industry.
“Manufacturers are challenged to make factories more efficient, safer and greener than ever before,” said Erik Walenza-Slabe, CEO, IoT One and Co-chair, IIC Smart Factory TG. “While no single organization can solve all the problems of the IIoT, the IIC is helping to revolutionize manufacturing through its many activities, including the innovations described in the third edition of the Journal of Innovation dedicated to the ‘Smart Factory.’”
New to this edition are two articles summarizing interviews with two IIC testbed leads, describing insights, outcomes and lessons learned. These articles highlight the innovations taking place in the Time Sensitive Networking (TSN) Testbed and the INFINITE Testbed.
“Testbeds are at the very core of what we do in IIC and we aim to feature testbeds in all of our future editions,” said Edy Liongosari, Chief Research Scientist of Accenture Labs and co-chair of the IIC Thought Leadership Task Group.
The Journal of Innovation includes the following articles authored by IIC member companies:
- “Blurry Box Encryption Scheme and Why it Matters to Industrial IoT”
- “Results, Insights and Best Practices from IIC Testbeds: Time Sensitive Networking (TSN) Testbed”
- “Making Factories Smarter through Machine Learning”
- “Driving Innovation in Product Design and Manufacturing using 3D Printing”
- “Results, Insights and Best Practices from IIC Testbeds: INFINITE Testbed”
- “Smart Factories and the Challenges of the Proximity Network”
Authors and interviewees within the third edition include Cisco, Cork Institute of Technology, Dell EMC Research Europe, Ikergune, IT Research Center, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Plethora IIoT, QualiCal, Synapse Wireless, System On Chip Engineering, Xilinx, Wibu-Systems.
by Gary Mintchell | Mar 3, 2016 | News, Organizations, Standards, Technology
 Interoperability among systems spurs economic and technological growth. Two of the leading proponents of new strategies for this next Industrial Revolution that we are beginning recently met.
Interoperability among systems spurs economic and technological growth. Two of the leading proponents of new strategies for this next Industrial Revolution that we are beginning recently met.
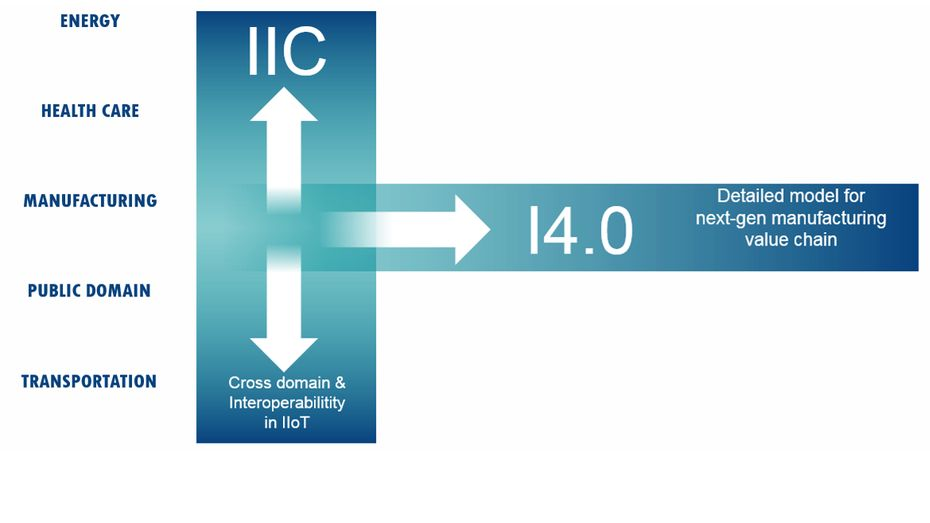
Representatives of Plattform Industrie 4.0 and the Industrial Internet Consortium met in Zurich, Switzerland to explore the potential alignment of their two architecture efforts – respectively, the Reference Architecture Model for Industrie 4.0 (RAMI4.0) and the Industrial Internet Reference Architecture (IIRA).
The meeting was a success, with a common recognition of the complementary nature of the two models, an initial draft mapping showing the direct relationships between elements of the models, and a clear roadmap to ensure future interoperability. Additional possible topics included collaboration in the areas of IIC Testbeds and I4.0 Test Facility Infrastructures, as well as standardization, architectures & business outcomes in the Industrial Internet.
The Zurich meeting was originally proposed by Bosch and SAP as members of the steering committees of both organizations. The meeting constituted an informal group which will continue their work on exploring potential alignment between I4.0 and IIC.
The open, informal discovery group included Bosch, Cisco, IIC, Pepperl + Fuchs, SAP, Siemens, Steinbeis Institute and ThingsWise.
Every press release these days, especially when it is an association of many members, includes the requisite quotes. Below are thoughts from some of the leaders.
Industry Reference Architecture Thought Leaders
State Secretary, Matthias Machnig, Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy: “We welcome the cooperation of both initiatives as an important milestone in the cooperation of companies internationally. The combined strengths of both IIC and Plattform Industrie 4.0 will substantially help to pave the way for a mutually beneficial development of a digitized economy for our international businesses.”
Prof. Dr. Siegfried Russwurm, Technical Director of Plattform Industrie 4.0, CTO and Member of the Managing Board of Siemens AG, said “Collaborating with other initiatives is important, especially for Germany’s export-oriented economy. We are highly interested to cooperate intensively with others in order to pave the way for global standards. Cooperating with IIC – and with other consortia – is an important step in the right direction”
Dr. Richard Mark Soley, Executive Director of the Industrial Internet Consortium, commented, “The effort shows that smart technical people can bridge any gap and find a way to solve problems that might otherwise have created barriers to entry in the adoption of IoT technology for industrial applications. I applaud the participants and thank them for their initial work, and look forward to a successful collaboration moving forward.”
Dr. Werner Struth, member of the Bosch board of management: “This is a huge accomplishment for industry adoption of the Industrial Internet of Things, as it will simplify technology choices immensely and lead to greatly enhanced interoperability.”
Bernd Leukert, Member of the SAP Executive Board emphasizes the importance of alignment between IIC and Plattform Industrie 4.0-initiated testbed initiatives: “This will allow for a much smoother international cooperation between smaller companies and larger enterprise to test out use cases and to initiate standards.”
Greg Petroff, Chief Experience Officer for GE Digital, said: “Breaking down the barriers of technology silos and supporting better integration of these architectures efforts will be key to advancing the Industrial Internet. This collaboration will help build a vibrant, united community around standards that drive integration toward solving the world’s toughest challenges.”
Robert Martin, Senior Principal Engineer in Cyber Security Partnership, The MITRE Corporation and member of the IIC Steering Committee, said “Bringing together the work of the Industrial Internet Consortium and the Plattform Industrie 4.0 Konsortium will dramatically increase the international value of both efforts and help to clarify and resolve the problems and concerns facing the global Industrial IoT marketplace quicker and more effectively than either could do alone.”
“I’m excited to see the two premier Industrial Internet of Things organizations aligning their efforts,” states Stan Schneider, CEO of Real-Time Innovations (RTI) and a member of the IIC Steering Committee. “Industrie 4.0’s strong foundation in industrial manufacturing and process combines well with the IIC’s emphasis on emerging IIoT applications in healthcare, transportation, power, and smart cities. We are working aggressively to align the connectivity infrastructures of the underlying DDS and OPC UA connectivity standards. We look forward to driving the rapid growth of the IIoT across all industries.”




 Committee co-chair Mark Crawford of the
Committee co-chair Mark Crawford of the 
 Interoperability among systems spurs economic and technological growth. Two of the leading proponents of new strategies for this next Industrial Revolution that we are beginning recently met.
Interoperability among systems spurs economic and technological growth. Two of the leading proponents of new strategies for this next Industrial Revolution that we are beginning recently met.



